Introduction
In today’s data-driven world, businesses are inundated with vast amounts of information. Managing this data efficiently has become a critical factor in an organization’s success. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore data management strategies that can pave the way for businesses to thrive in the digital age.
The Importance of Data Management
In the era of big data, data management is not merely a technical requirement but a strategic asset for businesses. Efficient data management Strategies can help organizations make informed decisions, improve customer experiences, and drive innovation.
Key Components of Data Management Strategies
Effective data management Strategies comprise several key components, including data governance, data quality, data storage, and data integration. Each plays a vital role in ensuring that data serves as a reliable resource rather than a hindrance.
Data Governance: Ensuring Data Quality
Data governance, as a crucial component of Data Management Strategies, involves establishing policies, processes, and standards for data management. It ensures data quality, accuracy, and compliance with regulatory requirements, building trust in the data.
Data Storage and Security
Secure and scalable data storage solutions are crucial for accommodating growing data volumes while safeguarding sensitive information from threats and breaches.
Data Integration: Breaking Down Silos
Data integration involves combining data from different sources to provide a unified view. This eliminates data silos, enhancing cross-functional collaboration and decision-making.
Master Data Management (MDM)
Master Data Management (MDM) is a crucial discipline that revolves around the creation and maintenance of a singular, reliable, and precise version of essential data, often referred to as “master data.” This master data typically encompasses critical information like customer details, product information, or any other core data entities that are fundamental to an organization’s operations.
MDM essentially acts as the guardian of an organization’s most valuable data assets, ensuring that these data elements remain consistent, trustworthy, and coherent across the entire enterprise. The primary objectives of MDM are to eliminate redundancies, discrepancies, and inaccuracies in master data, while also enabling data to be efficiently shared and utilized by various departments and systems within the organization.
Data Lifecycle Management
Data has a lifecycle, from creation to archival or disposal. Effective data lifecycle management ensures data remains relevant, accessible, and compliant throughout its journey.
Data Management Tools and Technologies
In the realm of data management, a rich tapestry of tools and technologies awaits organizations seeking to harness the power of their data assets. These tools are the linchpin of effective data management strategies, enabling businesses to store, process, analyze, and derive insights from their data. The selection of the right tools is pivotal, as it can significantly impact an organization’s ability to unlock the full potential of its data resources.
- Databases: Databases are the cornerstone of data management. They come in various flavors, including relational databases (SQL), NoSQL databases, and NewSQL databases. Each type serves specific purposes. Relational databases are ideal for structured data with well-defined schemas, while NoSQL databases excel in handling unstructured or semi-structured data. NewSQL databases offer a middle ground, combining the best of both worlds. Popular database systems like Oracle, MySQL, MongoDB, and Cassandra are widely used to store and manage data efficiently.
- Data Warehouses: Data warehousing solutions are designed to consolidate and store vast amounts of data from disparate sources. They enable organizations to perform complex queries and analysis on historical and real-time data. Amazon Redshift, Google BigQuery, and Snowflake are examples of cloud-based data warehouses that offer scalability and high performance for data analytics.
- Data Lakes: Data lakes are repositories that store data in its raw, unprocessed form. They are particularly suitable for storing vast volumes of raw data, including structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data. Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) and cloud-based data lakes like Amazon S3 and Azure Data Lake Storage are popular choices for organizations looking to harness the potential of big data.
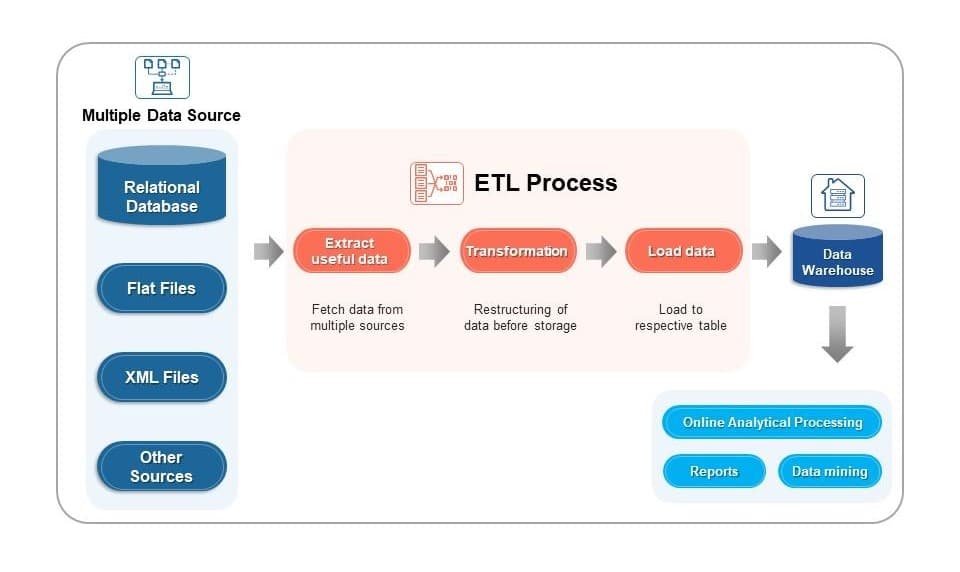
- Data Integration and ETL Tools: Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) tools play a pivotal role in data management by facilitating the movement of data between different systems, formats, and locations. Tools like Apache Nifi, Talend, and Informatica simplify the process of data extraction, transformation, and loading, ensuring data quality and consistency.
- Data Governance and Metadata Management: Effective data management goes hand in hand with robust data governance and metadata management tools. These tools help organizations define data ownership, enforce data quality standards, and track data lineage. Collibra and Informatica Axon are examples of platforms that empower businesses to govern their data effectively.
- Advanced Analytics and Machine Learning: Leveraging data for advanced analytics and machine learning requires specialized platforms. Tools like Python, R, and TensorFlow are essential for data scientists and analysts to build predictive models and gain valuable insights from data.
- Data Visualization and Business Intelligence (BI) Tools: Data visualization tools like Tableau, Power BI, and QlikView enable users to create interactive and insightful dashboards and reports. These tools transform raw data into actionable insights, aiding decision-makers in understanding trends and making informed choices.
Real-World Examples of Successful Implementation of Data Management Strategies
Explore real-world case studies of organizations that have effectively implemented data management strategies, showcasing the tangible benefits they achieved.
- Netflix’s Personalization Engine: Netflix employs robust data management to personalize content recommendations for its users. By analyzing viewing habits, user preferences, and feedback, they deliver tailored content, leading to higher user engagement and retention rates.
- Walmart’s Inventory Optimization: Walmart uses data management techniques to optimize inventory levels across its vast network of stores. Through real-time data analysis, they minimize overstocking and understocking issues, reducing carrying costs while ensuring products are available when needed by customers.
These examples demonstrate how effective data management strategies can drive business success by improving user experiences, reducing costs, and enhancing decision-making.
Conclusion: Building a Data-Driven Future
In conclusion, embracing robust data management strategies is not an option but a necessity for businesses aiming to thrive in the data-centric landscape. By implementing these strategies, organizations can unlock the full potential of their data, gain a competitive edge, and chart a path to success.
In this blog, we have delved into the world of data management, covering its significance, key components, governance, security, integration, and real-world examples. By following these data management strategies, businesses can harness the power of their data, drive innovation, and ensure a prosperous future in the digital age.