Introduction
The realm of data collection is vast and dynamic, encompassing a variety of strategies and techniques. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of data collection methods, offering insights and real-world examples to illustrate the effectiveness of these approaches. This blog not only serves as an educational resource but also as a practical guide for professionals and enthusiasts alike in the field of data analysis and research.
Our focus keyword for this exploration is ‘Data Collection Methods’, a term integral to the understanding and implementation of effective data-gathering strategies. As we navigate through the different aspects of this topic, we will see how these methods are applied in various scenarios, providing a rich context for their use.
Table of Contents
Understanding Data Collection
Data collection is a systematic process of gathering and measuring information on targeted variables in an established systematic fashion, which then enables one to answer relevant questions and evaluate outcomes. The process is essential in various fields, including business, healthcare, education, and social sciences, to name a few.
Effective data collection involves a combination of appropriate methods, clear objectives, and careful planning. It’s not just about accumulating data; it’s about gathering meaningful information that can drive decision-making and foster understanding.

Primary Data Collection Methods
Primary data collection involves gathering new data that has not been collected before. This can be done through various methods such as surveys, interviews, observations, and experiments. Each method has its strengths and is chosen based on the research question and the nature of the data required.
- Surveys: Used for collecting data from a large number of respondents. They can be conducted online, by phone, or in person.
- Interviews: In-depth data collection method, ideal for exploring complex issues. Can be structured, semi-structured, or unstructured.
- Observations: Involves collecting data through watching and recording behavior and activities.
- Experiments: Controlled tests to determine cause-and-effect relationships.
Real-time example: A market research company conducting surveys to understand consumer preferences for a new product.
Secondary Methods
The secondary method refers to the use of data that has already been collected and published by others. This includes sources like books, articles, journals, databases, and government reports. Secondary data is often used to gain a broader understanding of a topic or to supplement primary data.
- Public Records: Data from government agencies, such as census data.
- Academic Sources: Research papers, dissertations, and theses that provide detailed insights into specific topics.
- Commercial Sources: Data from businesses, such as market reports and sales data.
- Internet Sources: Online information including blogs, forums, and social media.
Real-time example: A researcher using census data to analyze demographic changes over the past decade.
Quantitative vs Qualitative Collection
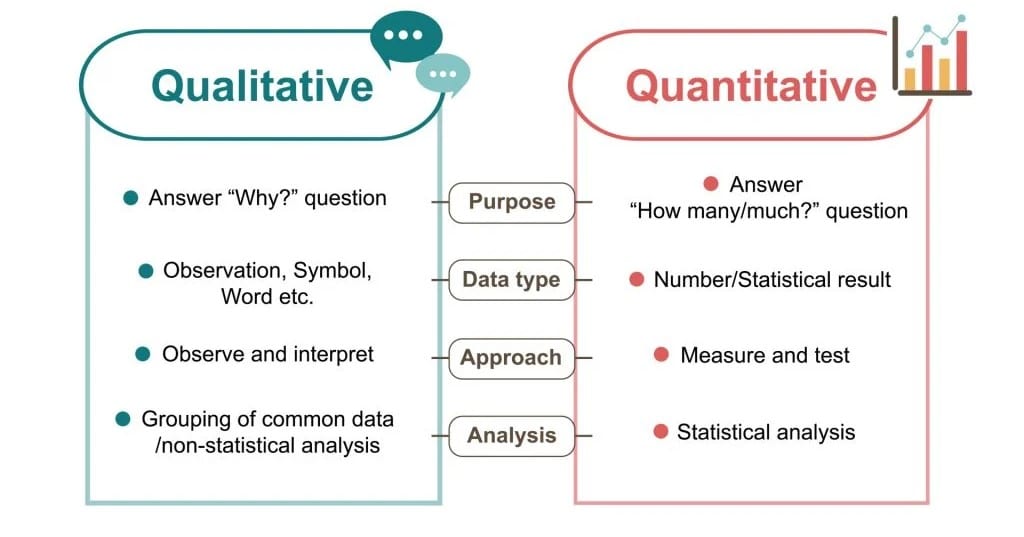
Methods of collecting data can be broadly categorized into quantitative and qualitative types. Quantitative methods involve the collection of numerical data that can be quantified and subjected to statistical analysis. Qualitative methods, on the other hand, focus on collecting non-numerical data, such as opinions, experiences, and observations, to gain deeper insights into the subject matter.
- Quantitative Methods: Surveys with closed-ended questions, experiments, and statistical analysis.
- Qualitative Methods: Interviews, focus groups, and content analysis.
Real-time example: A company conducting focus groups to understand customer sentiments about a new product feature.
Online Data Collection
In the digital age, online data collection has become increasingly prevalent. This method leverages the internet to gather information, offering a wide reach and the ability to collect large volumes of data efficiently. Online surveys, web analytics, social media monitoring, and online experiments are some of the key techniques used in this domain.
- Online Surveys: Convenient and cost-effective, allowing for a broad geographical reach.
- Web Analytics: Tracking and analyzing online user behavior and website traffic.
- Social Media Monitoring: Analyzing social media platforms to gather public opinions and trends.
- Online Experiments: Conducting controlled tests in a virtual environment.
Real-time example: A digital marketing agency using web analytics to track user engagement and improve website performance.
Ethical Considerations
While collecting data, it’s crucial to consider the ethical implications. This includes respecting privacy, obtaining consent, ensuring confidentiality, and being transparent about how the data will be used. Ethical data collection is not only a legal requirement in many cases but also a moral obligation to protect the rights and dignity of participants.
Real-time example: A healthcare research study obtaining informed consent from participants before collecting personal health information.
Challenges and Solutions in Data Collection
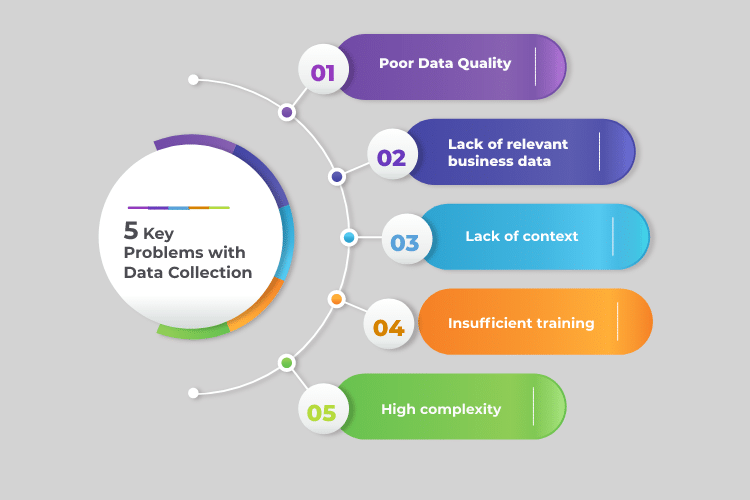
This is not without its challenges. Issues such as data quality, accessibility, and resource limitations can hinder the process. However, with the right strategies, these challenges can be overcome. Employing robust data validation techniques, ensuring accessibility and inclusivity in data collection methods, and leveraging technology for efficient data gathering are some of the key solutions.
Real-time example: A non-profit organization using mobile technology to collect data in remote areas, overcoming geographical barriers.
The Future of Data Collection
The future of the process is shaped by technological advancements and evolving methodologies. Emerging trends such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and the Internet of Things (IoT) are revolutionizing the way data is collected and analyzed. These technologies enable more efficient, accurate, and comprehensive data collection, opening new avenues for research and analysis.
Real-time example: Smart cities using IoT sensors to collect real-time data on traffic patterns, helping in urban planning and management.
Conclusion
In conclusion, data collection methods are a cornerstone of research and analysis in various fields. Understanding and applying the right strategies and techniques is crucial for the success of any data-driven project. As we move forward, the integration of technology and ethical practices in data collection will continue to play a significant role in shaping the landscape of research and decision-making processes.
This comprehensive guide has explored the different facets of data collection methods, providing insights and real-world examples to illustrate their application and effectiveness. Whether you are a seasoned professional or a newcomer to the field of data analysis, this guide serves as a valuable resource in your journey towards mastering data collection techniques.