Introduction
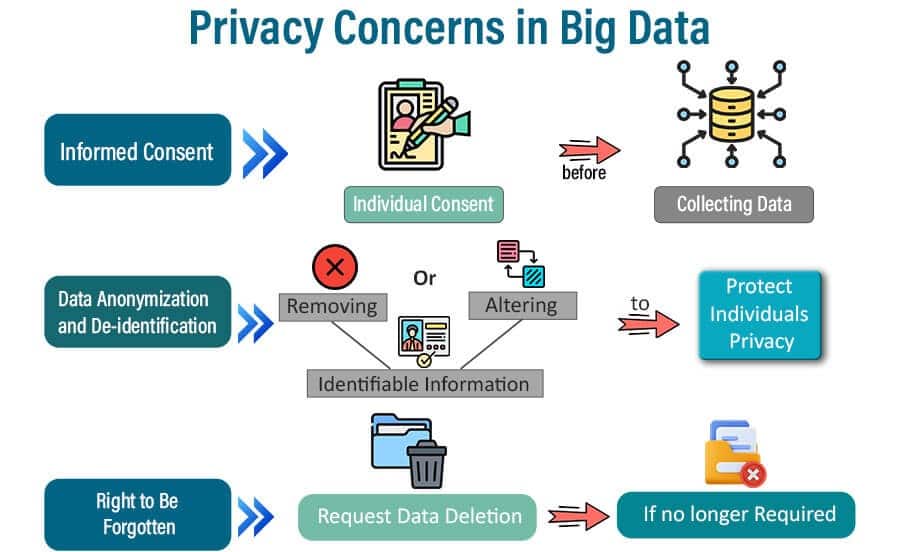
Welcome to ‘7 Key Principles of Data Ethics and Privacy in Data Handling,’ a comprehensive exploration of the ethical considerations in data management. This blog delves into the critical aspects of data ethics and privacy, discussing how organizations can responsibly handle data while respecting individual rights. We examine the balance between data utilization and privacy and the importance of ethical decision-making in data handling, with real-world examples of ethical dilemmas and resolutions in data management.
Data Migration to the Cloud
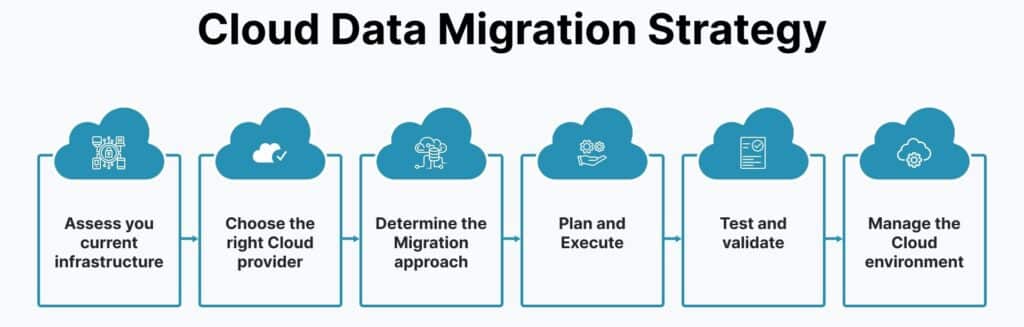
Migrating data to the cloud is a critical first step in modern data management. It involves careful planning and execution to ensure data integrity and minimize disruption. Effective strategies include phased data migration and using specialized data migration tools.
- Data Migration Challenges: Addressing compatibility, bandwidth limitations, and potential data loss is crucial for a smooth transition.
- Post-Migration Validation: Ensuring data integrity and completeness through testing and verification is essential after data migration.
Data Migration Challenges
Navigating the complexities of data migration involves addressing challenges such as data format compatibility, network bandwidth limitations, and potential data loss. Effective strategies must be in place to mitigate these risks, ensuring a seamless transition to the cloud environment.
Post-Migration Validation
After migrating data to the cloud, it’s crucial to validate the integrity and completeness of the data. This process involves thorough testing and verification to ensure that the data migration has been successful and that the data is accurately and fully represented in the cloud.
Cloud Storage Solutions
Selecting the right cloud storage solution is key to effective data management. It involves understanding different storage types and balancing factors like cost, scalability, and accessibility.
Evolving Storage Technologies: The cloud storage landscape is continuously evolving, with new technologies offering improved performance, enhanced security, and better cost-efficiency. Staying abreast of these developments is crucial for businesses to make informed decisions about their cloud storage strategies.
Customizable Storage Options: Many cloud providers offer customizable storage options, allowing businesses to tailor their storage solutions according to specific needs, such as compliance requirements, access frequency, and budget constraints.
Data Security and Compliance in the Cloud

Data security and compliance are paramount in cloud data management. Implementing robust security measures and ensuring adherence to regulations are critical for protecting sensitive data.
Emerging Security Threats: Integration with Data Migration Strategies
As cloud technologies advance, so do the security threats targeting them. Businesses must be vigilant and proactive in adopting the latest security measures and technologies to protect their data against evolving cyber threats.
As cloud storage technologies evolve, their integration with data migration strategies becomes increasingly important. Advanced storage solutions now offer features like automated data transfer and synchronization, making the migration process more efficient and less prone to errors. Businesses looking to migrate their data to the cloud can benefit from these advancements, ensuring a smoother transition and better alignment with their overall data management objectives.
Compliance as an Ongoing Process: Facilitating Seamless Data Migration
Compliance with data protection regulations is not a one-time task but an ongoing process. Regular audits, updates to security protocols, and staying informed about changes in data protection laws are essential to maintain compliance.
Customizable storage options play a crucial role in facilitating seamless data migration. Providers that offer flexibility in storage types, such as object, block, or file storage, enable businesses to choose solutions that best fit their data migration needs. This adaptability is particularly beneficial for companies migrating diverse data sets, as it allows for a more tailored approach, ensuring that each type of data is stored optimally for both current use and future scalability.
Cloud Data Analytics
Leveraging cloud data analytics involves using powerful tools for processing and gaining insights from large datasets. It enables predictive analytics, real-time analysis, and big data processing.
- Real-Time Analytics Capabilities: Cloud platforms increasingly offer real-time analytics capabilities, enabling businesses to gain instant insights from their data. This immediacy can be a game-changer in decision-making processes and operational efficiency.
- Scalability of Analytics Solutions: One of the significant advantages of cloud data analytics is scalability. Businesses can scale their analytics capabilities up or down based on their changing needs, ensuring they have the right resources at the right time.
Integrating Cloud Data with Business Processes
Integrating cloud data with business processes enhances operational efficiency and decision-making. It involves using APIs and integration tools for seamless connectivity.
- Streamlining Business Operations: Effective integration of cloud data with business processes can significantly streamline operations, reduce manual interventions, and enhance overall productivity.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: Integrating cloud data into business processes facilitates data-driven decision-making. Businesses can leverage real-time data insights to make informed decisions, enhancing their agility and competitive edge.
Conclusion
Data ethics and privacy in data handling are fundamental to building trust in the digital age. Embracing these principles ensures compliance and establishes businesses as responsible entities. The future of data handling will integrate ethics and privacy into all data-related activities, fostering a secure and ethical digital ecosystem.
In conclusion, the principles of data ethics and privacy in data handling are not just regulatory requirements but are fundamental to building trust and integrity in the digital age. As technology continues to evolve, so does the landscape of data ethics and privacy. Businesses that proactively embrace these principles will not only ensure compliance but also establish themselves as responsible and trustworthy entities in the eyes of their customers and the public. The future of data handling is one where ethics and privacy become integral to all data-related activities, driving a more secure and ethical digital ecosystem.



Howdy! dataexpertise.in
Did you know that it is possible to send requests correctly lawfully? We are offering a legitimate way of sending requests via feedback forms.
Since they are deemed vital, messages sent through Feedback Forms are not classified as spam.
We are now offering you the chance to use our service for free.
We will transmit up to 50,000 messages to you.
The cost of sending one million messages is $59.
This message was automatically generated.
We only use chat for communication.
Contact us.
Telegram – https://t.me/FeedbackFormEU
Skype live:contactform_18
WhatsApp – +375259112693
WhatsApp https://wa.me/+375259112693
Great work! This is the type of info that should be shared around the internet.
Shame on the seek engines for now not positioning this post upper!
Come on over and discuss with my website . Thanks =)
Thanks for the Comment!