Introduction
Welcome to our in-depth exploration of edge computing in the Internet of Things (IoT). As the digital world generates data at an unprecedented scale, edge computing has emerged as a crucial technology. It enables faster, more efficient processing of data at its source, revolutionizing the IoT landscape. This blog delves into the key aspects of edge computing in IoT, discussing its benefits, challenges, and real-world applications.
- Focus on Edge Computing in IoT: Understanding its transformative role.
- Decentralized Data Processing: How edge computing is reshaping data handling.
The Rise of Edge Computing in IoT
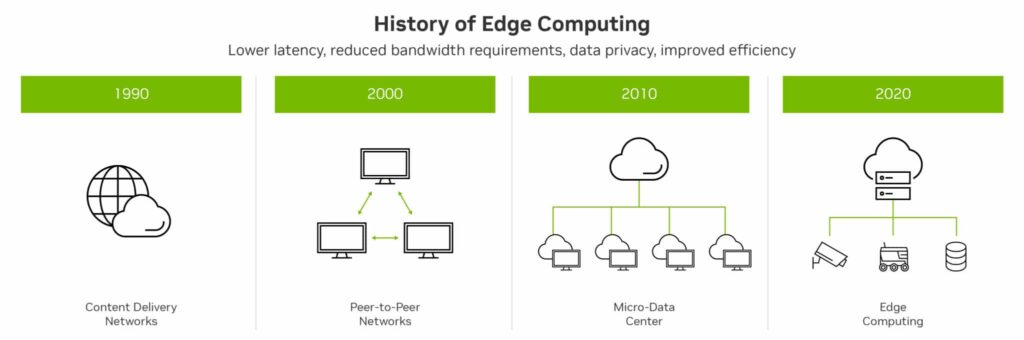
Edge computing marks a significant shift in data processing, bringing computation closer to data sources. This approach reduces latency, enhances response times, and minimizes bandwidth usage.
- Reducing Latency: How it speeds up data processing.
- Real-world Example: Edge computing in smart city infrastructure.
The adoption of this technology in IoT is not just a trend; it’s a strategic shift in data processing. By enabling real-time data processing at the edge of the network, devices can act on data insights more quickly and efficiently. This immediacy is crucial in applications like autonomous vehicles and real-time remote monitoring, where every millisecond counts. The integration of the technology in IoT devices is paving the way for smarter, more responsive, and autonomous systems, driving innovation across various industries.
Enhanced Security and Privacy
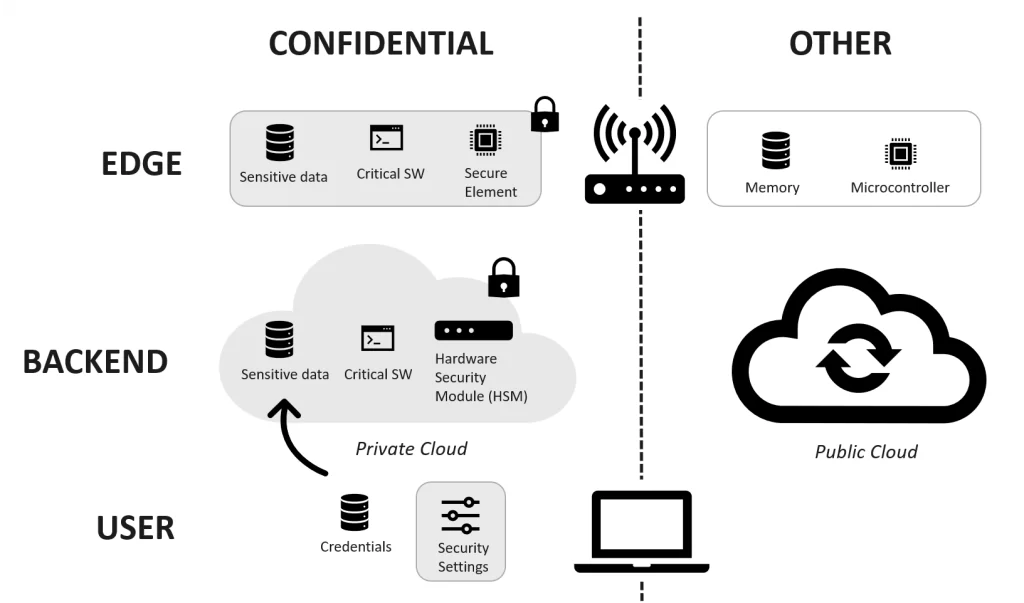
By processing data locally, edge computing offers enhanced security and privacy, crucial for sensitive IoT applications. Edge computing’s approach to processing data locally significantly mitigates the risks associated with data transit.
- Local Data Processing: Its impact on security and privacy.
- Case Study: In healthcare data management.
By reducing the amount of sensitive data traversing through the network, the vulnerability to cyber-attacks and data breaches is substantially lowered. This localized processing is particularly beneficial in sectors like finance and defense, where data security is paramount. Furthermore, it aids in compliance with data privacy regulations, as data can be processed and stored within the geographical boundaries where it’s generated.
Scalability and Flexibility in IoT
Edge computing provides scalability and flexibility, allowing IoT networks to adapt to varying demands and conditions. The scalability and flexibility offered by this are vital in managing the explosive growth of IoT devices. As the number of connected devices continues to rise, it provides a sustainable way to handle this increase without overburdening the network.
This scalability ensures that IoT systems can grow and adapt without compromising performance or efficiency. Additionally, the flexibility of the technology allows for the deployment of customized solutions tailored to specific industry needs, enhancing the overall effectiveness of IoT applications.
- Adapting to Demand: How it scales with IoT needs.
- Example: Flexible data processing in industrial IoT.
Reduced Bandwidth and Cost Savings
With local data processing, edge computing significantly reduces the need for bandwidth, leading to cost savings.
- Bandwidth Efficiency: Minimizing data transmission costs.
- Real-world Application: Cost-effective solutions in remote monitoring.
By processing data locally and reducing the need to send vast amounts of data back to a central server, it significantly cuts down on bandwidth usage. This reduction not only leads to cost savings in terms of data transmission but also reduces the strain on network infrastructure. For businesses, this means lower operational costs and a more efficient use of resources. In remote or rural areas, where bandwidth is limited or expensive, this technology becomes an even more critical component in ensuring the viability and sustainability of IoT solutions.
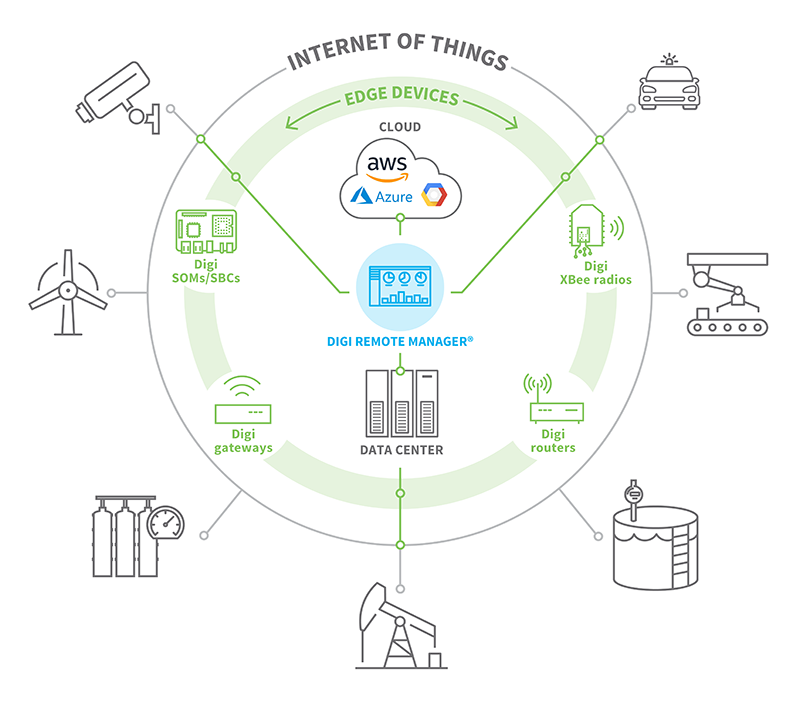
Challenges and Future Prospects
While it offers numerous benefits, it also presents challenges such as the need for advanced hardware and the complexity of integrating with existing systems. Ensuring the reliability and maintenance of devices is another challenge, especially in remote or inaccessible locations.
However, as technology advances, these challenges are being addressed through innovations in hardware design and software solutions. The future in IoT looks promising, with ongoing research and development poised to overcome these hurdles and fully unlock its potential.
- Overcoming Challenges: Navigating the hurdles in edge computing.
- Future Outlook: The evolving role of edge computing in IoT.
Conclusion
Edge computing is a game-changer in IoT, offering decentralized data processing that enhances efficiency, security, and scalability. As we continue to advance in the IoT era, the role of edge computing will become increasingly vital.
- Transforming IoT: The pivotal role of edge computing.
- Looking Ahead: The promising future of edge computing in IoT.
In conclusion, it is revolutionizing the IoT landscape by bringing data processing closer to where it’s needed most. This paradigm shift not only enhances efficiency and responsiveness but also opens up new possibilities for IoT applications. As we move forward, the continued evolution of edge computing will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping the future of IoT, driving advancements in various sectors and creating a more connected and intelligent world.



