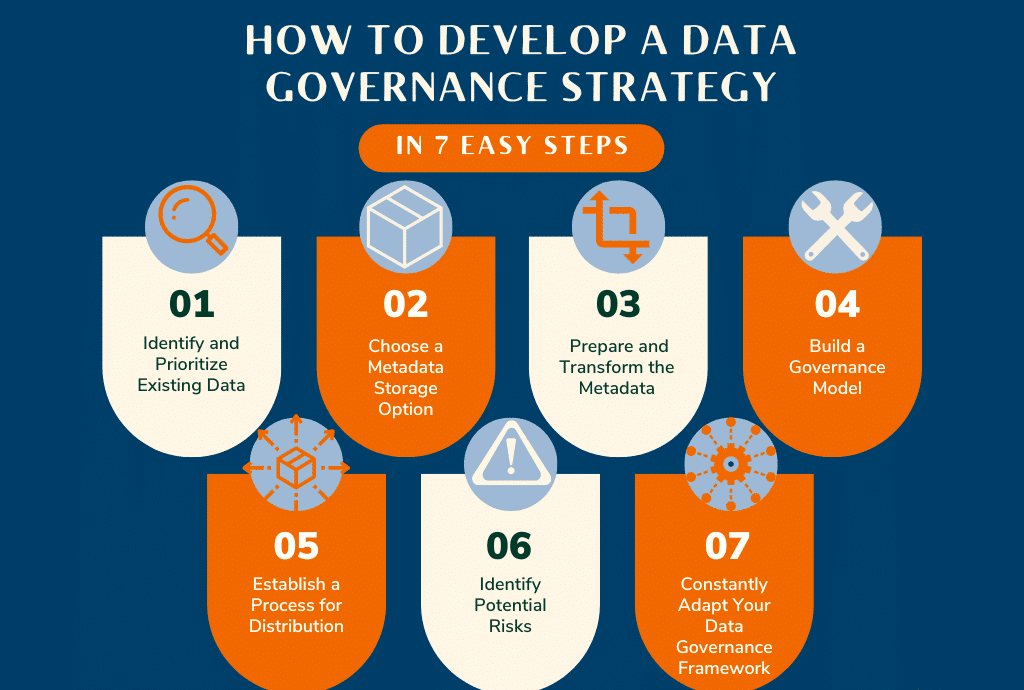
Introduction
In the digital age, effective data governance is not just a necessity but a strategic asset for organizations. It ensures data accuracy, enhances privacy, and drives strategic decision-making. This comprehensive guide, distilled from the wisdom of data management experts, outlines actionable strategies for robust data governance.
Establishing a Clear Data Governance Framework
Objective Setting: Begin by defining clear, measurable objectives for your effective data governance initiative. What are your goals? Improved data quality, regulatory compliance, enhanced decision-making?
- Roles and Responsibilities: Establish clear roles and responsibilities. This includes appointing data stewards, defining their duties, and establishing an effective data governance committee to oversee governance initiatives.
- Expert Insight: Effective Data governance frameworks should be tailored to the specific needs and culture of the organization. They must be flexible enough to adapt to changing data landscapes and business objectives.
Managing Data Quality
Data Quality Monitoring: Implement continuous data quality monitoring mechanisms. Use tools and technologies to automate data cleansing, validation, and deduplication processes. Beyond monitoring and improvement plans, managing data quality also involves embedding quality checks at every stage of data collection and processing.
This proactive approach ensures that data issues are identified and rectified at the source, minimizing downstream errors and enhancing the reliability of business insights. Engaging all stakeholders in the importance of high-quality data and its impact on decision-making can further reinforce data quality initiatives.
- Data Quality Improvement Plans: Develop and execute data quality improvement plans. Identify the root causes of data issues and implement corrective measures.
- Expert Insight: Consistent data quality management is foundational for operational efficiency and analytical accuracy. It requires a proactive approach, integrating quality control measures throughout the data lifecycle.
Ensuring Data Security and Privacy
Data Security Policies: Develop comprehensive data security policies. Ensure they align with global standards and regulatory requirements.

Data security and privacy extend beyond compliance; they are about building trust with customers and stakeholders. Implementing advanced encryption, regular security audits and incident response plans are crucial. Equally important is fostering a culture where every employee understands their role in protecting data, recognizing that security and privacy are collective responsibilities that underpin the organization’s integrity and reputation.
- Privacy Compliance: Stay updated with data privacy laws and regulations. Implement data protection measures that comply with GDPR, CCPA, and other relevant frameworks.
- Expert Insight: Data security and privacy should be ingrained in the organization’s culture. Regular training and awareness programs can help foster a proactive stance on data privacy.
Leveraging Technology for Data Governance
Technology Integration: Utilize advanced data management platforms and tools. Integrate AI and machine learning to automate data governance tasks and gain deeper insights. While technology plays a pivotal role in effective data governance, it’s essential to ensure that it complements rather than complicates the governance framework.
The integration of technology should be strategic, with a focus on enhancing data accessibility, improving data quality, and providing actionable insights. It’s also vital to regularly assess the effectiveness of these technological tools in meeting the organization’s data governance objectives, ensuring they remain aligned with evolving business needs.
Data Governance Dashboards: Develop dashboards to monitor effective data governance metrics. Use these tools to track progress, identify issues, and make informed decisions.
Expert Insight: Technology should be seen as an enabler of effective data governance, not a replacement for strategic planning and human oversight. Choose solutions that align with your governance objectives and organizational capabilities.
Fostering an Effective Data Governance Culture
Promoting Data Literacy: Encourage data literacy across the organization. Provide training and resources to help employees understand data governance’s value and their role in it.
- Collaboration and Communication: Foster a collaborative environment where data governance is a shared responsibility. Regular communication can help align various departments with governance goals.
- Expert Insight: A data governance culture is built on understanding, trust, and collaboration. It requires ongoing effort and commitment at all levels of the organization.
Creating a data governance culture is an ongoing process that requires continuous engagement and education. It’s about instilling a sense of ownership and accountability for data across all levels of the organization. Encouraging open dialogue about data challenges and successes can help demystify data governance and integrate it into the daily workflow, ensuring that it becomes an intrinsic part of the organizational ethos rather than a set of imposed rules.
Continuous Improvement in Data Governance
Regular Reviews: Conduct regular reviews of your effective data governance policies and practices. Adapt to new business needs, technological advancements, and regulatory changes.
Feedback Loops: Establish mechanisms to gather feedback from stakeholders. Use this feedback to refine and improve your data governance strategies.
Expert Insight: Data governance is an evolving discipline. An organization’s ability to adapt and respond to new challenges is key to sustaining effective governance.
Conclusion
Data governance is a critical component of modern business strategy. By adopting these expert-recommended strategies, organizations can ensure their data governance frameworks are robust, adaptable, and aligned with their business objectives. The journey toward effective data governance is ongoing, requiring commitment, adaptability, and a proactive approach to managing one of the organization’s most valuable assets: its data.




