Introduction to Advanced Data Collection
In our rapidly digitizing world, the ability to gather, analyze, and leverage data has become a cornerstone of success across all industries. Advanced data collection is not merely about accumulating vast amounts of information but about doing so efficiently, accurately, and in a way that is actionable for businesses and organizations. This blog explores the cutting-edge methods and tools that are shaping the future of data collection, offering insights into their applications and the advantages they bring.
The Significance of Data in Today’s World
Data is often referred to as the new oil, underscoring its value in the modern economy. From predicting consumer behavior to driving technological innovation, the applications of data are vast and varied. In healthcare, data can mean the difference between life and death, while in finance, it can predict market trends and guide investment strategies. The significance of data is such that it influences decision-making at all levels, shaping policies, strategies, and everyday operations.
Overview of Advanced Data Collection Methods
IoT Sensors and Devices
IoT sensors and devices are at the forefront of transforming how data is collected, offering real-time insights into a myriad of processes. In agriculture, for instance, IoT sensors monitor soil moisture levels, informing irrigation practices and enhancing crop yields. In manufacturing, these sensors track equipment performance, predicting failures before they occur and reducing downtime.
Big Data Analytics
Big data analytics allows organizations to sift through enormous datasets to identify trends, patterns, and anomalies. This method is instrumental in sectors like retail, where understanding consumer preferences can help tailor products and services, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Machine Learning and AI
AI and machine learning are redefining data collection by automating complex processes, enhancing the accuracy of data collected, and offering predictive insights. These technologies can analyze data from various sources, identifying patterns that would be impossible for human analysts to detect.
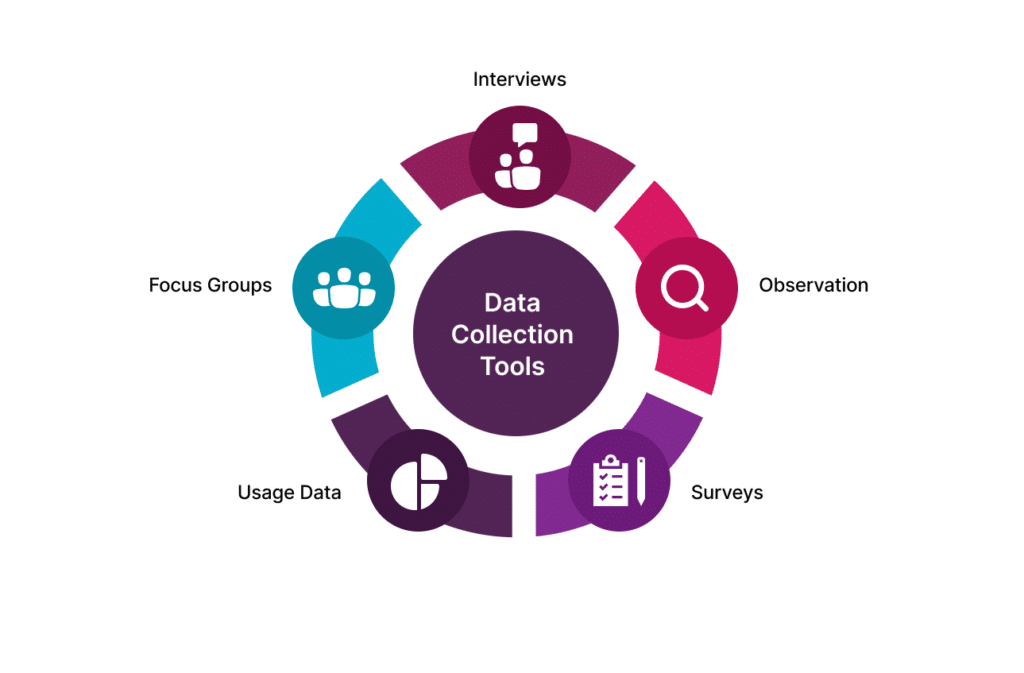
Tools for Effective Data Collection
The landscape of data collection is rich with tools designed to capture, organize, and analyze data across various domains. These tools range from Data Management Platforms (DMPs) that aggregate and analyze data from multiple sources, to Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems that provide insights into customer behaviors and preferences. Additionally, survey and feedback tools offer direct channels to gather consumer perceptions and needs, providing a wealth of qualitative and quantitative data. The choice of tools is critical, as it directly influences the quality of data collected, the efficiency of data processing, and the depth of insights that can be derived, ultimately impacting decision-making and strategic direction.
Data Management Platforms (DMPs)
DMPs are essential for organizations dealing with vast amounts of data from diverse sources. They not only help in collecting and organizing data but also in analyzing it, providing a comprehensive platform for data-driven decision-making.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems
CRMs are pivotal in understanding customer interactions and behaviors. They track customer journeys, preferences, and feedback, enabling businesses to tailor their offerings and enhance customer experiences.
Survey and Feedback Tools for Data Collection
Surveys and feedback tools are crucial for direct engagement with customers or audiences. These tools provide valuable insights into customer needs, expectations, and perceptions, informing product development, marketing strategies, and customer service approaches.
Real-Time Examples of Data Collection Success
Healthcare Monitoring
In healthcare, real-time data collection from wearable devices can monitor patient health metrics, alerting medical professionals to potential issues before they become critical. This proactive approach can save lives, reduce hospital stays, and improve overall health outcomes.
Retail Analytics
In retail, data analytics can track customer buying patterns, inventory levels, and market trends. This information helps retailers optimize their stock levels, improve customer engagement, and increase sales.
Smart Cities
Smart cities leverage data from various sensors and devices to improve urban living. Traffic management, waste disposal, energy use, and public safety are just a few areas where data collection and analysis can significantly enhance efficiency and quality of life.
Linking Data Collection to Data Analysis
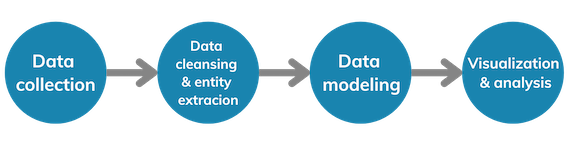
The true value of data collection lies in the analysis. Without proper analysis, data remains a raw, untapped resource. This section explores how data collection and analysis are intrinsically linked, with the analysis phase turning collected data into actionable insights that can inform strategic decisions, drive innovations, and solve complex problems.
While data collection is a critical step, its true value is realized through data analysis, where raw data is transformed into actionable insights. This linkage is vital for businesses seeking to drive decision-making and strategy with data. Analysis elucidates patterns, trends, and correlations in the collected data, providing a foundation for predictive modeling and decision-making. Here are key points illustrating this linkage:
- Data Interpretation: Translating raw data into a format that is understandable and useful for making decisions.
- Trend Identification: Recognizing patterns within the data that may indicate opportunities or risks.
- Predictive Analysis: Using historical data to forecast future outcomes, helping in proactive decision-making.
- Strategic Insights: Deriving meaningful insights that can guide business strategy and operational improvements.
Tips for Maximizing Data Accuracy and Integrity
Maintaining the accuracy and integrity of collected data is paramount. This section provides practical tips on ensuring data quality, from implementing robust data governance frameworks to conducting regular data audits and training team members on best practices in data management and analysis.
Ensuring the accuracy and integrity of data is paramount for any organization that relies on data-driven decision-making. Inaccurate or corrupted data can lead to misguided strategies and poor outcomes. Below are strategies to enhance data accuracy and integrity:
- Implement Data Governance: Establish clear policies and protocols for data collection, storage, and usage.
- Conduct Regular Audits: Regularly review and validate the data to ensure its accuracy and consistency.
- Data Cleaning: Regularly remove or correct inaccurate, incomplete, or irrelevant data from the dataset.
- User Training: Ensure team members are trained in best practices for data collection and handling to minimize errors.
The Future of Data Collection
Looking ahead, the future of data collection is set to be even more intertwined with AI, ML, and IoT, driving greater automation, accuracy, and insight. This section delves into the emerging trends and technologies that are shaping the future of data collection, highlighting how they can enable more dynamic, responsive, and informed decision-making processes.
The future of data collection is shaped by rapid advancements in technology, with emerging trends promising to revolutionize how we gather and interpret data. Here are pivotal points that highlight the future trajectory of data collection:
- Increased Automation: Leveraging AI and machine learning for automated data collection and analysis, reducing human error and increasing efficiency.
- Real-Time Data: The growth of IoT and connected devices will enable real-time data collection and analysis, offering instant insights and the ability to act swiftly.
- Data Privacy and Ethics: As data collection capabilities expand, so will the focus on ethical considerations and data privacy, ensuring data is collected and used responsibly.
- Integration of Diverse Data Sources: Future tools will likely offer more sophisticated integration of varied data sources, providing a more holistic view and richer insights.
Conclusion
As we’ve explored throughout this blog, enhancing data collection with advanced methods and tools is crucial for unlocking the transformative power of data. By embracing these innovative approaches, organizations can not only improve their operational efficiency and decision-making but also gain a competitive edge in the ever-evolving digital landscape.
In conclusion, the integration of advanced data collection methods and tools is not merely an enhancement of processes but a transformative step towards building a data-driven organizational culture. This evolution is essential in an era where data is a critical asset in navigating the complexities of the digital landscape. By adopting these sophisticated approaches, organizations empower themselves with the ability to make informed decisions, predict future trends, and respond dynamically to market changes.
Ultimately, the commitment to advanced data collection is a commitment to continuous improvement, innovation, and maintaining a competitive edge in an increasingly data-centric world, ensuring organizations not only survive but thrive in the digital age.





