Introduction to Emotional AI
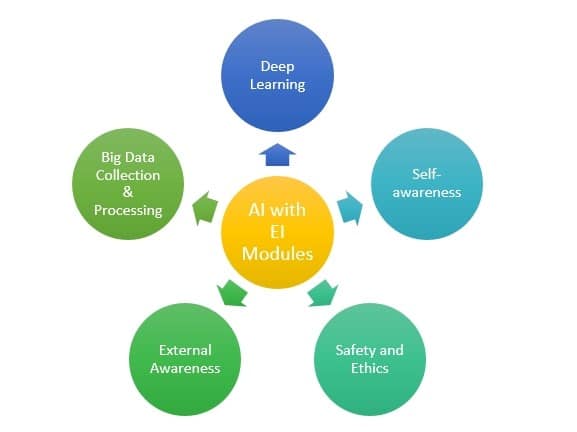
Emotional Artificial Intelligence (Emotional AI), also known as affective computing, is an emerging field that aims to enable machines to interpret, process, and simulate human emotions. Unlike traditional sentiment analysis, which typically categorizes emotions into basic sentiments, Emotional AI delves deeper into the nuanced spectrum of human emotions, offering a more sophisticated and holistic understanding of emotional states.
Emotional AI stands at the forefront of bridging the gap between human emotions and artificial intelligence. By enabling machines to understand and respond to human emotions, it is setting a new standard for how we interact with technology, making it more intuitive, responsive, and ultimately, more human-like.
The Evolution from Sentiment Analysis to Emotional AI
While sentiment analysis has provided valuable insights into consumer behavior and preferences, it often falls short in capturing the complexity of human emotions. It represents a significant advancement, employing sophisticated algorithms and neural networks to detect and analyze a broader array of emotional cues and responses.
This evolution marks a shift from binary sentiment interpretation to a multidimensional emotion understanding, reflecting the complexity and depth of human emotional expression. Emotional AI’s rise signifies a move towards more empathetic and context-aware technologies, reshaping how AI understands and engages with us on a daily basis.
- Complex Emotion Recognition: Beyond positive, negative, or neutral.
- Contextual Understanding: Interpreting emotions within context.
Key Components of Emotional AI
To function effectively, these AI systems incorporate several key components, including natural language processing, facial expression detection, voice intonation analysis, and physiological signal processing, each contributing to a comprehensive emotional understanding.
To accurately interpret human emotions, Emotional AI leverages various components, each addressing different aspects of emotion recognition and processing.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP allows Emotional AI to understand and interpret human language, detecting emotional nuances in text to gauge sentiments and emotional states.
Facial Expression Analysis
This component analyzes facial cues to identify emotions, using computer vision to interpret expressions and respond appropriately.
Voice Intonation Analysis
By examining tone, pitch, and pace, this component deciphers emotions conveyed through voice, enhancing the AI’s understanding of the user’s emotional state.
Physiological Signal Processing
Sensors detecting physiological signals like heart rate or skin conductance provide additional context, enabling a deeper analysis of emotional states.
Real-world applications of Emotional Artificial Intelligence
Emotional Artificial Intelligence is finding its way into various sectors, enhancing customer service, healthcare, marketing, and entertainment. For example, it’s being used in customer service bots to respond to user emotions effectively, and in healthcare to monitor patient emotional states for better treatment outcomes.
From enhancing user experience in tech products to providing critical insights in healthcare, Emotional AI’s applications are vast and varied.
- Customer Service: Improving interaction through emotion-aware customer service bots.
- Automotive: Enhancing driver safety by monitoring emotional states.
- Education: Personalizing learning experiences based on students’ emotional responses.
Integrating Emotional Artificial Intelligence with Existing Technologies
The integration of Emotional AI with technologies like IoT, big data, and VR is opening up new frontiers. For instance, VR experiences can be enhanced with Emotional AI to adapt in real-time to users’ emotional states, creating more immersive and personalized experiences.
The integration of Emotional AI into existing technologies is creating more adaptive, user-centered systems that respond to individual emotional cues.
- Smart Homes: Adjusting environments based on occupants’ emotions.
- Wearable Tech: Providing feedback on emotional well-being.
- Entertainment: Tailoring content to viewers’ emotional responses.
Why Emotional AI Matters in the Modern World
Human emotions influence almost every aspect of decision-making, communication, and behavior. Traditional AI, focused on logic and structured data, often misses this crucial human element. Emotional AI addresses this gap, making technology more adaptive, empathetic, and human-centric.
Key benefits include:
- Enhanced Human-Machine Interaction: Devices respond appropriately to moods, frustration, or excitement.
- Improved Productivity: In workplaces, emotion-aware systems can optimize workflows based on user engagement and stress levels.
- Better Healthcare Outcomes: Emotional AI can detect early signs of depression, anxiety, or stress, allowing for timely intervention.
Advanced Techniques in Emotional AI
While core components like NLP, facial recognition, and voice analysis form the backbone, advanced Emotional AI uses sophisticated techniques to achieve higher accuracy:
1. Multimodal Emotion Recognition
Humans express emotions through multiple channels: speech, text, facial expression, body language, and physiological signals.
- Emotional AI integrates these multiple modalities to achieve a more precise understanding of emotional states.
- Example: Combining voice tone, micro-expressions, and wearable heart-rate data to detect stress levels in employees.
2. Deep Learning and Neural Networks
Deep learning models such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) for facial expression analysis and Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs)/Transformers for speech and text allow Emotional AI to learn subtle patterns.
- These models can detect micro-emotions that are not apparent to human observers.
- Example: Detecting subtle cues of sarcasm or frustration in customer service calls.
3. Sentiment and Contextual Understanding
Emotions are rarely isolated—they are influenced by context, prior interactions, and cultural factors.
- Emotional AI employs context-aware sentiment analysis, using history, situational context, and user profile data to improve interpretation.
- Example: Understanding that “I’m fine” may signal distress depending on previous emotional interactions.
4. Predictive Emotional Analytics
Beyond detecting current emotions, Emotional AI can predict emotional responses based on patterns over time.
- This enables proactive interventions in areas like mental health, customer service, or education.
- Example: Predicting student engagement or fatigue in virtual classrooms for personalized learning adjustments.
Emerging Applications of Emotional AI
1. Healthcare and Wellbeing
- Mental Health Monitoring: Detecting depression, anxiety, or PTSD from voice patterns, text, or facial expressions.
- Patient Engagement: Emotion-aware telehealth systems improve remote consultation experiences.
2. Customer Experience
- Emotionally Intelligent Chatbots: Bots respond empathetically, improving resolution rates and customer satisfaction.
- Personalized Marketing: Tailoring product recommendations and promotions based on detected emotional state.
3. Automotive Industry
- Driver Safety: Monitoring fatigue, stress, or anger to prevent accidents.
- Passenger Experience: Adjusting cabin settings (lighting, music) according to mood.
4. Education and E-Learning
- Adaptive Learning Systems: Emotional AI detects frustration or boredom to modify content delivery.
- Teacher Assistance Tools: Providing real-time feedback on student engagement in virtual classrooms.
5. Entertainment and Media
- Content Personalization: Emotion-aware streaming platforms recommend movies, shows, or music based on viewer mood.
- Immersive VR/AR Experiences: Games and VR experiences adapt dynamically to player emotional responses.
Key Challenges in Emotional AI
While Emotional AI holds great promise, it also faces technical and ethical challenges:
- Data Privacy and Security
- Emotional data is highly sensitive. Unauthorized access or misuse can have severe consequences.
- Solutions: End-to-end encryption, anonymization, and strong consent protocols.
- Emotional data is highly sensitive. Unauthorized access or misuse can have severe consequences.
- Cultural and Individual Variability
- Expressions of emotion vary across cultures and individuals.
- AI models need diverse datasets to avoid misinterpretation.
- Expressions of emotion vary across cultures and individuals.
- Bias and Fairness
- AI systems may inherit biases from training data, misclassifying emotions in certain groups.
- Continuous auditing and inclusive training datasets are critical.
- AI systems may inherit biases from training data, misclassifying emotions in certain groups.
- Ambiguity of Human Emotions
- Emotions are often subtle, mixed, and context-dependent, making them difficult to detect accurately.
- Emotions are often subtle, mixed, and context-dependent, making them difficult to detect accurately.
- Ethical Concerns
- Manipulation risk: Using emotional data for persuasion in marketing or politics.
- Consent and transparency are vital to maintaining trust.
- Manipulation risk: Using emotional data for persuasion in marketing or politics.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations in Emotional Artificial Intelligence
While promising, Emotional AI raises significant ethical concerns, including privacy, consent, and the potential for manipulation. Ensuring transparency, accountability, and user control is paramount in the development and deployment of Emotional AI systems.
As Emotional AI advances, it raises critical ethical questions that need addressing to ensure its responsible development and deployment.
- Privacy: Ensuring user data, especially emotional data, is protected.
- Consent: Users must have control over when and how their emotional data is used.
- Transparency: Users should understand how emotional data influences AI behavior.
- Privacy and Consent: Safeguarding personal emotional data.
- Bias and Fairness: Addressing potential biases in emotion recognition.
Case Studies: Emotional Artificial Intelligence in Action
Emotional AI’s impact is already being felt across various industries, demonstrating its potential to revolutionize traditional practices.
Case Study 1: Emotional Artificial Intelligence in Retail
Explore how a major retail brand uses Emotional AI to tailor customer experiences, resulting in increased satisfaction and loyalty. Beyond enhancing customer experiences, Emotional AI in retail is paving the way for more personalized marketing strategies and improved customer engagement, leading to increased loyalty and sales.
Case Study 2: Emotional Artificial Intelligence in Mental Health
Discover how Emotional AI is revolutionizing mental health support, offering new ways to diagnose and treat emotional disorders.
In mental health, Emotional AI is not just a tool for diagnosis; it’s becoming an integral part of ongoing care, offering new ways to monitor, understand, and interact with patients, potentially transforming mental health treatment.
The Future of Emotional AI
The future of Emotional AI is promising, with advancements likely to result in more intuitive, empathetic, and interactive AI systems. However, the pace of technological growth must be matched with robust ethical frameworks and user-centric approaches.
As Emotional AI continues to evolve, its future promises even greater integration into our daily lives, offering new possibilities for interaction and understanding between humans and machines.
- Enhanced Empathy: Machines will offer more nuanced emotional responses.
- Wider Adoption: Emotional AI will become commonplace across more sectors.
- Deeper Integration: More seamless blending with IoT, wearables, and more.
Advanced Techniques for Improving Emotional AI Accuracy
- Transfer Learning: Leveraging pre-trained models from one domain (e.g., facial emotion datasets) to another, reducing training costs.
- Attention Mechanisms: Highlighting relevant features in speech or facial patterns for better emotional detection.
- Generative Models: Using GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks) to simulate emotional responses for training data augmentation.
- Continuous Learning: Emotional AI models adapt in real-time to new user behaviors, improving personalization.
Conclusion
Emotional Artificial Intelligence represents a groundbreaking shift in how we interact with machines, offering profound possibilities for enhancing human-AI interaction. As we advance, balancing innovation with ethical responsibility will be crucial.
Emotional AI represents a significant leap forward in the AI journey, offering a glimpse into a future where technology not only understands but also empathizes with us, creating a more connected and emotionally intelligent world.
FAQ’s
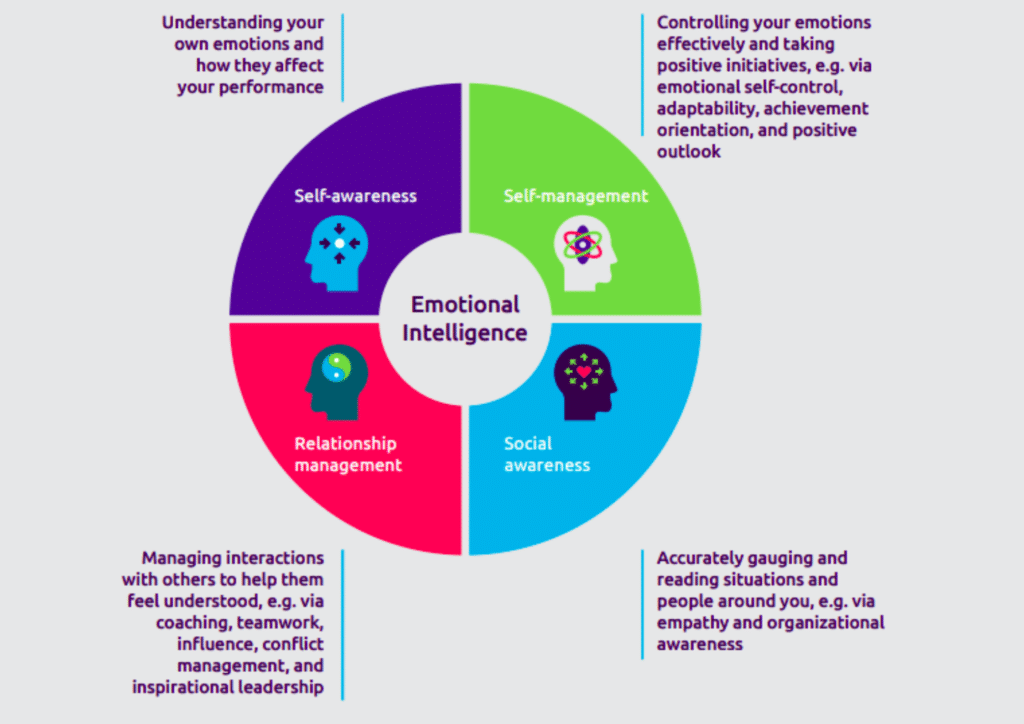
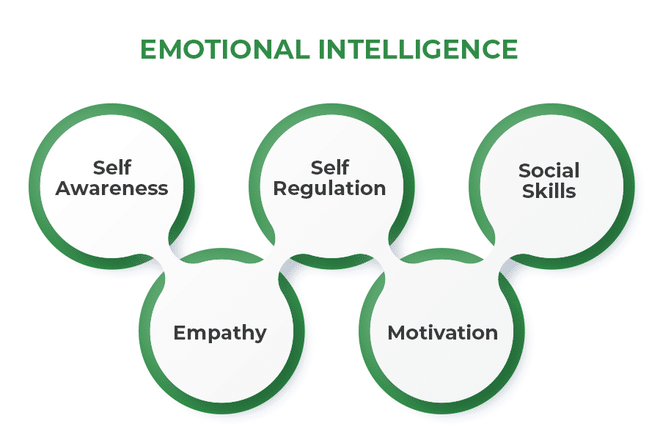
What are the 4 types of emotional intelligence?
The four types of emotional intelligence are self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, and relationship management, enabling individuals or AI systems to understand and manage emotions effectively.
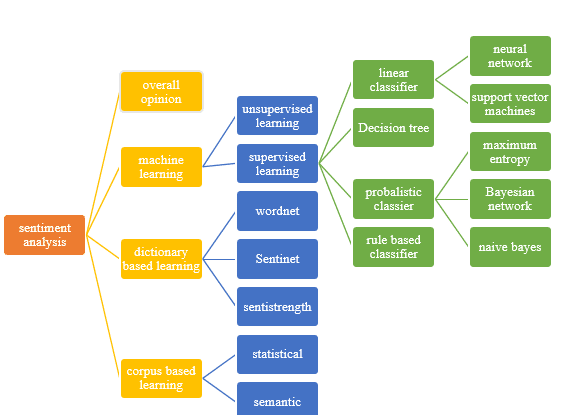
Can AI be used for sentiment analysis?
Yes, AI can be used for sentiment analysis by processing text, speech, or social media data to detect emotions, opinions, and attitudes, helping businesses and researchers understand public sentiment.
What are the 5 C’s of emotional intelligence?
The 5 C’s of emotional intelligence are self-awareness, confidence, self-control, commitment, and communication, which help individuals recognize, manage, and express emotions effectively in personal and professional settings.
How does artificial intelligence apply to emotional intelligence?
AI applies to emotional intelligence by analyzing and interpreting human emotions from text, speech, and facial expressions, enabling machines to respond empathetically, improve user interactions, and support decision-making in emotionally sensitive contexts.
What are the 4 pillars of emotional intelligence?
AI applies to emotional intelligence by analyzing and interpreting human emotions from text, speech, and facial expressions, enabling machines to respond empathetically, improve user interactions, and support decision-making in emotionally sensitive contexts.



