Introduction
In an era where digital information flows incessantly, the imperative for robust data compliance has never been more pronounced. Organizations across the globe are finding themselves at a crossroads, where the need to harness data for operational excellence must be balanced with the imperative to protect individual privacy rights.
- Delve into the criticality of data compliance in today’s digital landscape, where data breaches and privacy concerns are escalating.
- Examine the widespread impact of stringent regulations like GDPR and CCPA on businesses worldwide, emphasizing the shift towards more transparent data practices.
The advent of comprehensive data regulations such as GDPR and CCPA marks a significant pivot in the business world, compelling companies to reevaluate and fortify their data handling procedures. These regulations are not just legal frameworks but catalysts for a broader movement toward transparency and accountability in data management. They signal a departure from the laissez-faire attitude of the past, steering businesses towards a future where data privacy is not just a compliance requirement but a core facet of corporate integrity and customer trust.
Understanding GDPR: A Global Benchmark
The GDPR’s far-reaching provisions have ushered in a new era of data privacy, setting a high bar for data protection globally. By mandating explicit consent for data processing, enforcing the principle of data minimization, and requiring prompt notifications in the event of a data breach, GDPR has reshaped how organizations interact with personal data. Its impact extends beyond the European Union, affecting any entity that deals with the data of EU residents, thereby influencing global data management practices.
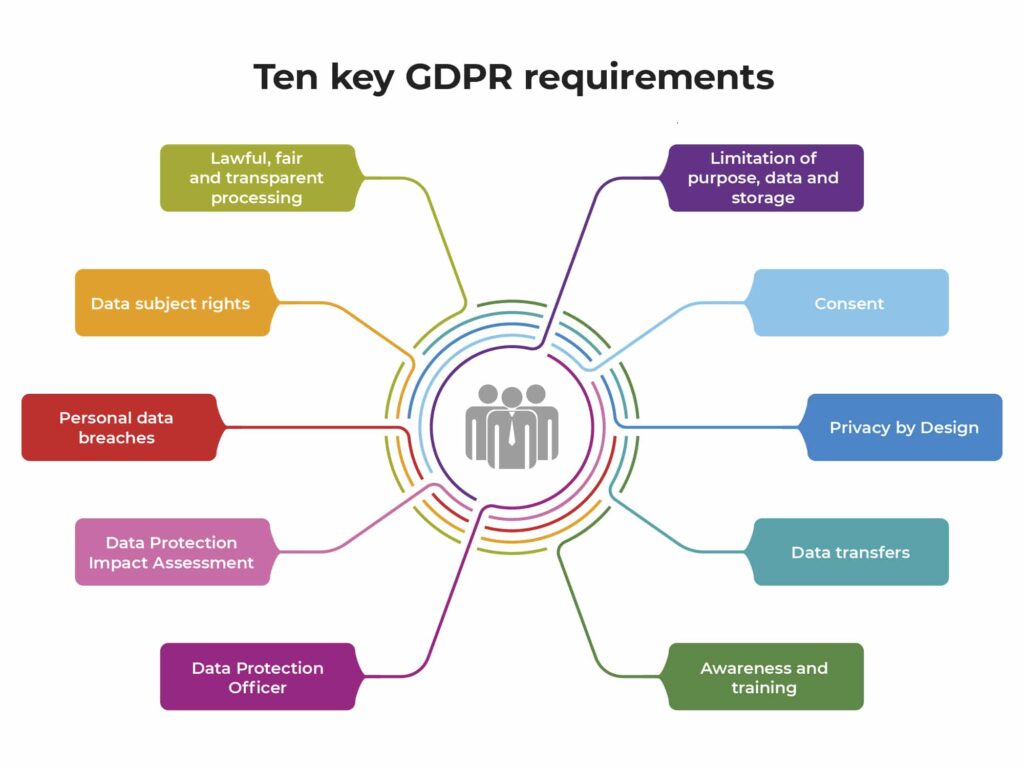
Organizations are now tasked with a comprehensive set of compliance obligations, from enhancing data security measures to ensuring the rights of data subjects are upheld, all while maintaining a clear record of their data processing activities. The substantial penalties for non-compliance underscore the regulation’s emphasis on accountability and the high stakes for businesses in the digital age, making GDPR compliance a top priority for organizations worldwide.
- Key Provisions: GDPR sets stringent data protection standards, mandating consent, data minimization, and timely breach notifications.
- Scope and Impact: Affects any organization worldwide that processes data of EU citizens, fundamentally changing global data handling practices.
- Compliance Obligations: Organizations must implement comprehensive data protection measures, ensure data subject rights, and maintain transparent data processing records.
- Penalties: Non-compliance can result in hefty fines, up to 4% of annual global turnover or €20 million, whichever is higher.
Navigating the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
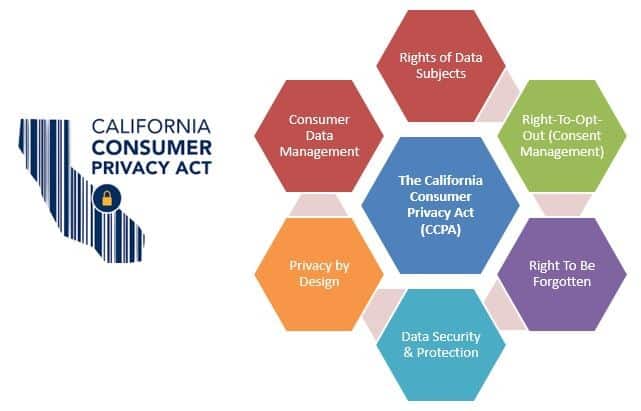
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) revolutionizes data privacy, giving consumers unprecedented control over their personal information and setting strict transparency requirements for businesses. This landmark legislation not only enhances consumer rights but also places new, rigorous obligations on companies to manage and protect personal data responsibly.
- CCPA Requirements: Introduces data transparency, grants consumers the right to know about data collection, and the power to request data deletion.
- Consumer Rights: Californians can now access their data, understand its usage, and opt out of data selling.
- Business Duties: Businesses must disclose data collection practices, respond to consumer data requests, and ensure data protection measures.
- Penalties: Violations can lead to fines and enforcement actions, emphasizing the need for stringent data compliance.
Expanding Horizons: Emerging Global Data Privacy Regulations
The global data privacy landscape is rapidly evolving, with countries like Brazil implementing the LGPD and India developing its own data protection framework, reflecting a worldwide shift towards stronger data privacy measures.
- Overview of Global Trends: Beyond GDPR and CCPA, regulations like Brazil’s LGPD and India’s proposed framework are shaping the global data privacy landscape.
- Comparative Analysis: These laws vary in scope and requirements but share common goals in enhancing data transparency and user control.
While these laws differ in specifics, they collectively underscore a global movement towards enhancing data transparency and empowering individuals with greater control over their personal information.
Developing a Comprehensive Data Compliance Strategy
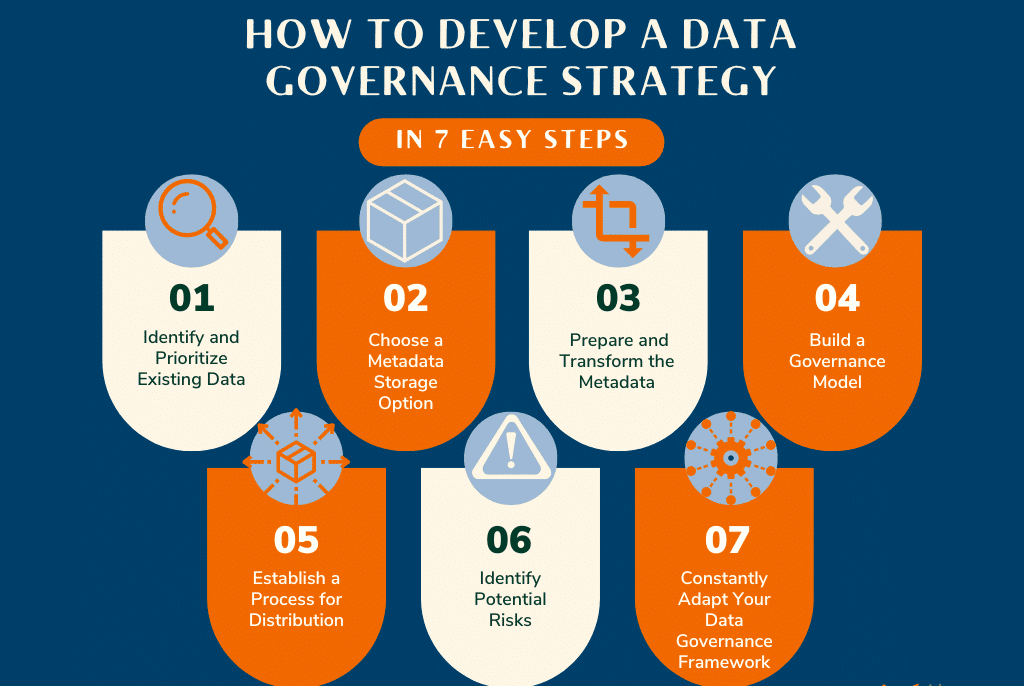
Crafting a data compliance strategy is pivotal for organizations aiming to navigate the intricate web of global data regulations. A well-defined strategy not only aligns with legal requirements but also fortifies trust with stakeholders, ensuring data is handled with the utmost integrity and care.
- Steps for Strategy Development: Start with a data audit, define compliance objectives, and develop a cross-functional compliance team.
- Role of Technology: Leverage technology for data mapping, automated compliance checks, and to streamline data subject request processes.
- Continuous Monitoring: Establish ongoing monitoring and updating mechanisms to adapt to evolving data protection regulations and emerging risks.
Leveraging Data Compliance for Competitive Advantage
- Trust Building: Demonstrating compliance can significantly enhance consumer trust and loyalty in an era where data privacy is a key concern.
- Market Differentiation: Use data compliance as a differentiator, showcasing a commitment to data protection as a core business value.
In the realm of data compliance, businesses have a unique opportunity to turn regulatory adherence into a competitive edge. Companies that excel in data compliance can enhance their reputation, foster customer loyalty, and differentiate themselves in a marketplace where consumers are increasingly data-conscious.
Overcoming Challenges in Data Compliance
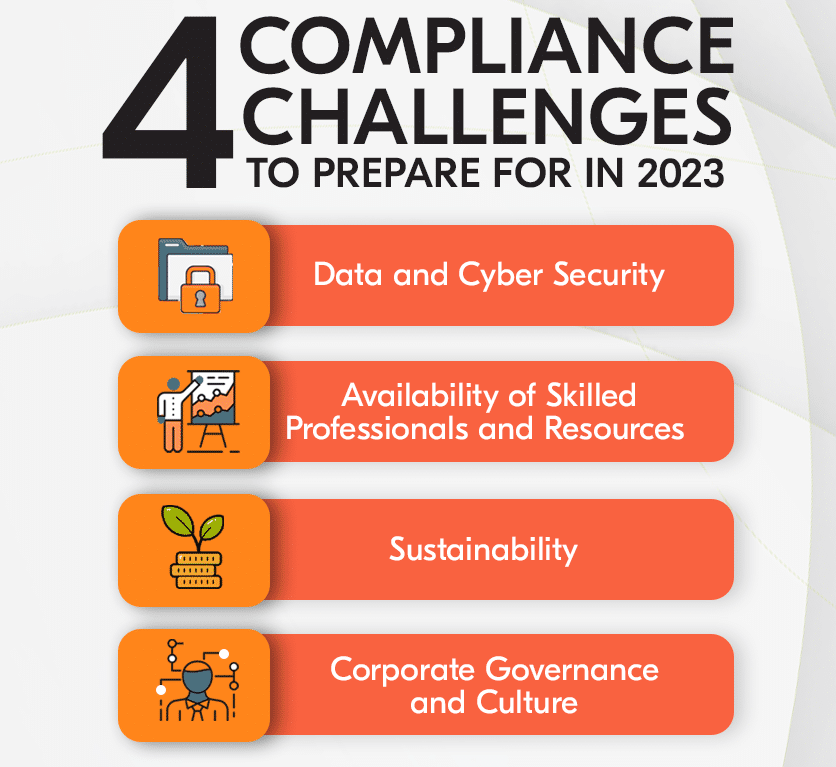
Addressing the challenges in data compliance demands a proactive approach, where organizations anticipate potential hurdles and devise strategic solutions. By transforming compliance challenges into opportunities for improvement, businesses can establish a resilient framework that supports sustainable growth and innovation.
- Common Obstacles: Challenges include keeping up with rapidly changing regulations, ensuring cross-departmental collaboration, and managing complex data landscapes.
- Best Practices: Address these challenges through continuous education, investing in compliance technologies, and fostering a culture of data privacy within the organization.
Conclusion
Data compliance is not merely a legal obligation; it’s a cornerstone of modern business ethics that plays a crucial role in safeguarding organizations against legal risks. By adhering to data compliance standards, companies can build and maintain trust with their customers, a vital asset in today’s digital economy.
This trust is foundational for sustaining a competitive edge, as consumers are increasingly favoring businesses that demonstrate a commitment to data privacy and security. In essence, data compliance is an investment in an organization’s reputation and operational resilience, mitigating risks and fostering a culture of transparency and accountability.
In this dynamic digital landscape, where regulations and societal expectations are continually evolving, businesses must adopt a proactive stance toward data compliance. Staying ahead of the curve requires a commitment to ongoing education, regular policy reviews, and the flexibility to adapt strategies in response to new legislative developments and emerging best practices.
By embracing a forward-thinking approach to data compliance, businesses can not only ensure they meet the current standards but also future-proof their operations against upcoming changes, thereby securing their position as trusted leaders in their respective industries.



