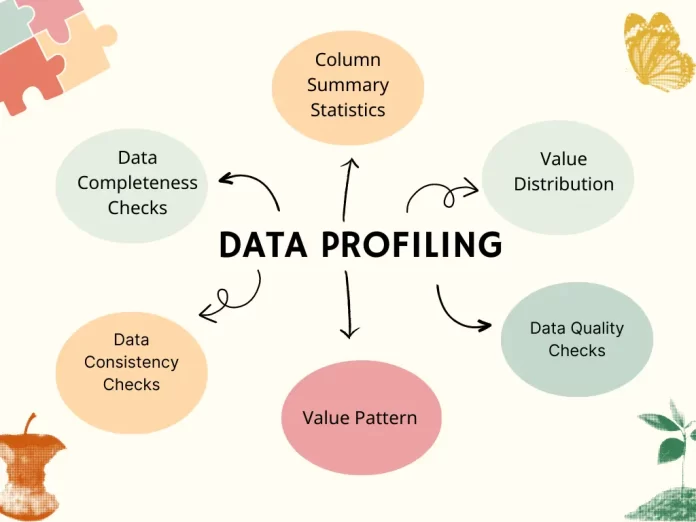
Introduction to Data Profiling
Data profiling is a crucial process in modern data management that involves examining and analyzing data to ensure its quality, consistency, and integrity. It plays a vital role in identifying issues, patterns, and relationships within data, which can significantly impact business decision-making and strategic planning. Below is a breakdown of key points and sub-points related to data profiling, each accompanied by descriptive paragraphs and bullet points for clarity.
Definition of Data Profiling
Data profiling is the process of systematically reviewing data to understand its structure, content, and quality. It involves collecting statistical summaries about datasets to gain insights into data characteristics such as distribution, consistency, and integrity. This process is essential for identifying data quality issues and ensuring that data is suitable for analysis and decision-making.
Key Activities in Data Profiling:
- Data Type Identification: Determining the data types (e.g., integer, string, date) within datasets.
- Pattern Recognition: Discovering recurring patterns and formats in the data (e.g., phone number formats, email structures).
- Anomaly Detection: Identifying outliers, duplicates, and inconsistent data entries.
- Data Quality Assessment: Evaluating data’s completeness, accuracy, and validity.
Data profiling helps organizations understand the actual content of their datasets. Organizations can detect anomalies and inconsistencies early in the data lifecycle by examining the statistical properties of data, such as the frequency distribution, average values, and variance. This early detection is crucial for maintaining data quality and ensuring the information used for business decisions is accurate and reliable.
Importance of Data Profiling in Modern Data Management
Data profiling is a critical aspect of data management because it ensures that the data used for analysis and decision-making is highly quality. Inaccurate or inconsistent data can lead to poor business decisions, resulting in financial losses, regulatory non-compliance, and reputational damage.
Benefits of Data Profiling:
- Improves Data Quality: Helps identify and rectify errors in the dataset, ensuring data accuracy and reliability.
- Facilitates Data Integration: It makes combining data from different sources easier by understanding the structure and content of each dataset.
- Enhances Compliance: Supports regulatory compliance by ensuring data meets industry standards and legal requirements.
- Supports Decision Making: Provides accurate data insights that form the basis of strategic business decisions.
The role of data profiling extends beyond just ensuring data quality; it also plays a vital part in enhancing data governance and compliance. By systematically analyzing data, organizations can create a solid foundation for data management strategies, which helps in maintaining regulatory compliance and building customer trust. In industries such as healthcare, finance, and telecommunications, where data accuracy is paramount, data profiling serves as a safeguard against potential data breaches and compliance issues.
Overview of How Data Profiling Fits into the Data Lifecycle
Data profiling is integrated into various stages of the data lifecycle, including data collection, preparation, storage, and analysis. By incorporating data profiling early and throughout the data lifecycle, organizations can maintain high data quality standards.
Stages Where Data Profiling is Applied:
- Data Collection: Profiling helps understand the data being collected from various sources, ensuring that only high-quality data enters the system.
- Data Preparation: Identifies data quality issues that need to be addressed, such as missing values and inconsistencies.
- Data Storage: Ensures that data stored in databases and data warehouses is consistent, accurate, and ready for use.
- Data Analysis: Provides insights into data patterns and trends, supporting more accurate and effective data analysis.
Data profiling is not a one-time activity but a continuous process that aligns with the entire data lifecycle. From the initial collection of raw data to its preparation for analysis and storage, data profiling provides ongoing insights into data quality and integrity. This proactive approach allows organizations to address data quality issues as they arise, ensuring that their data assets remain reliable and useful throughout their lifecycle. By integrating data profiling into their data management practices, organizations can maximize the value of their data and maintain a robust data governance framework.
Importance of Data Profiling in Data Management
Data profiling plays a vital role in effective data management by ensuring the integrity, accuracy, and reliability of data within an organization. By systematically analyzing and assessing data, organizations can gain valuable insights that enhance the quality of their data, ensure compliance with regulations, streamline integration processes, reduce costs, and improve decision-making. Below are key areas highlighting the importance of data profiling in data management.
Enhancing Data Quality
Data quality is foundational to the success of any data-driven organization. Data profiling enables organizations to identify inconsistencies, inaccuracies, and anomalies within their datasets. By regularly conducting data profiling, companies can ensure that their data is clean, accurate, and reliable. This process not only improves the overall quality of the data but also increases trust in data-driven insights and analytics.
- Consistency Checks: Data profiling ensures that data formats and structures are consistent across different datasets, reducing the risk of errors.
- Accuracy Verification: It helps in identifying and correcting inaccuracies, such as outdated information or typos, which can skew analysis.
- Completeness: Profiling ensures that all required data fields are populated, and missing data is identified and rectified.
Supporting Regulatory Compliance
In today’s regulatory environment, ensuring data compliance is crucial for avoiding legal penalties and maintaining customer trust. Data profiling helps organizations adhere to regulatory standards by identifying and rectifying data issues that could lead to non-compliance.
- Data Protection Regulations: Profiling helps ensure data is processed by privacy laws, such as GDPR or HIPAA, by flagging sensitive information and ensuring its protection.
- Audit Readiness: Regular data profiling prepares organizations for audits by ensuring that data is accurate, complete, and well-documented, thereby demonstrating compliance with relevant regulations.
Facilitating Data Integration
As organizations increasingly rely on multiple data sources, integrating diverse datasets into a unified view becomes critical. Data profiling aids in the seamless integration of data by analyzing the structure and content of different datasets, identifying discrepancies, and ensuring compatibility.
- Schema Matching: By understanding the schema of different datasets, data profiling helps in aligning fields and attributes for smooth integration.
- Data Harmonization: Profiling aids in standardizing data formats and structures, making it easier to merge and reconcile data from various sources.
Data profiling is essential for efficient data integration, especially in large organizations where data is collected from multiple systems and departments. By identifying inconsistencies and redundancies early, data profiling ensures that integration efforts are smooth and that the resulting datasets are accurate and meaningful. This streamlines data processing and analysis, leading to more reliable business intelligence.
Reducing Operational Costs
By identifying and addressing data quality issues proactively, data profiling helps organizations avoid costly mistakes and rework. Poor data quality can lead to erroneous decision-making, which may result in financial losses, inefficiencies, and missed opportunities.
- Reduced Error Rates: Early detection of data errors reduces the time and resources spent on manual data cleaning and correction.
- Improved Efficiency: Streamlining data management processes through regular profiling minimizes the need for extensive data audits and troubleshooting, saving both time and money.
Improving Decision-Making and Strategic Planning
High-quality data is critical for effective decision-making and strategic planning. Data profiling provides organizations with insights into the state of their data, enabling them to make informed decisions based on accurate and complete information.
- Data-Driven Insights: Profiling ensures that the data used for analysis is accurate and reliable, providing a solid foundation for deriving actionable insights.
- Strategic Alignment: Understanding data quality helps organizations align their strategies with data-driven goals, ensuring that business decisions are based on factual and up-to-date information.
In the competitive business landscape, strategic decisions must be based on solid data. Data profiling helps organizations maintain data quality, ensuring that leaders have access to accurate information. This enables companies to respond quickly to market changes, optimize operations, and plan for the future with confidence. By incorporating data profiling into their regular data management practices, businesses can enhance their strategic capabilities and maintain a competitive edge.
Key Concepts in Data Profiling
Understanding the key concepts of data profiling is essential for maintaining high data quality standards and ensuring the accuracy and reliability of data. These concepts help organizations identify, analyze, and rectify data issues, leading to improved data management and decision-making processes. Here are the fundamental concepts in data profiling:
Data Accuracy
Data accuracy refers to the degree to which data correctly reflects the real-world objects or events it is intended to represent. Accurate data is crucial for making informed business decisions and maintaining the integrity of analytical insights.
- Verification: Data profiling techniques can verify the correctness of data entries, identifying errors such as incorrect values, misreporting, or typos.
- Correction: Profiling tools often provide mechanisms to correct inaccuracies, ensuring that data remains valid and useful.
Ensuring data accuracy is foundational for any data-driven organization. Inaccurate data can lead to erroneous conclusions and misguided strategies. By regularly profiling data for accuracy, organizations can maintain trust in their data and its insights, thereby supporting effective decision-making and operational efficiency.
Data Completeness
Data completeness measures whether all required data is present in a dataset. Incomplete data can lead to biased analysis and incomplete insights, which may impact decision-making.
- Missing Data Detection: Data profiling helps in identifying missing values and records, ensuring that all necessary data is collected and available for analysis.
- Data Filling: Profiling can also suggest methods to fill in missing data, either through imputation techniques or by flagging gaps for further investigation.
Data completeness is vital for holistic analysis and accurate reporting. Incomplete data can result in misleading insights, compromising the reliability of analytics. By focusing on completeness during data profiling, organizations can ensure they have all the necessary information for comprehensive analysis and reporting.
Data Consistency
Data consistency refers to the uniformity of data across different datasets and systems. Consistency is critical for data integration and aggregation, ensuring that data from various sources aligns properly.
- Standardization: Profiling helps in standardizing data formats, units of measure, and naming conventions across different datasets.
- Conflict Resolution: Data profiling tools can identify and resolve inconsistencies, such as conflicting values or duplicate entries, which might arise when data is collected from multiple sources.
Maintaining data consistency is essential for effective data integration and interoperability. Consistent data allows for seamless merging of datasets from various sources, enhancing the accuracy of aggregated data and enabling reliable cross-system analytics. Regular data profiling ensures that consistency is upheld across all data assets.
Data Uniqueness
Data uniqueness refers to the distinctiveness of data entries within a dataset. Unique data is critical for accurate identification and tracking of individual records, especially in customer databases and transaction logs.
- Duplicate Detection: Profiling identifies duplicate records that can distort analysis and reporting.
- Unique Key Validation: Ensuring that unique identifiers (such as customer IDs or transaction numbers) are genuinely unique within the dataset.
Data uniqueness is a key aspect of maintaining data quality, particularly in databases where individual records need to be tracked precisely. Profiling for uniqueness helps prevent redundancy and ensures the integrity of datasets, which is critical for customer relationship management, financial transactions, and inventory control.
Data Timeliness
Data timeliness refers to how up-to-date and relevant the data is. Timely data is essential for making real-time decisions and for processes that rely on current information.
- Timestamp Validation: Profiling checks the timestamps of data entries to ensure that data is recent and relevant.
- Frequency Monitoring: Monitoring data updates to ensure that data is refreshed at appropriate intervals to remain useful for analysis.
In the fast-paced business environment, the timeliness of data can significantly impact decision-making. Data profiling ensures that data is current and relevant, supporting timely decisions and actions. Timeliness is especially important in sectors like finance and healthcare, where outdated information can have serious consequences.
Data Integrity
Data integrity ensures that data is accurate, consistent, and reliable over its entire lifecycle. It encompasses various dimensions, including accuracy, consistency, and completeness, to maintain the trustworthiness of data.
- Referential Integrity: Profiling checks relationships between different data entities, ensuring that foreign keys and other relational data constructs maintain their integrity.
- Validation Rules: Data integrity is supported by enforcing validation rules that check the correctness and coherence of data entries.
Data integrity is the cornerstone of reliable data management, ensuring that data remains accurate and consistent throughout its lifecycle. Profiling for integrity helps prevent data corruption and maintains the reliability of databases, which is crucial for maintaining stakeholder trust and compliance with data governance standards.
Types of Data Profiling Techniques
Data profiling techniques vary depending on the specific requirements and goals of the data analysis. Each type focuses on different aspects of data quality and integrity, helping organizations maintain a high standard of data management. Below are some of the most commonly used data profiling techniques:
Column Profiling
Column profiling involves analyzing data within a single column of a dataset to understand its structure and content. It identifies distinct values, frequency distribution, and other metrics that provide insights into the data.
- Definition and Examples: This technique examines individual columns to determine the types of data present, the range of values, and the frequency of each value. For example, profiling a customer database column might reveal how many distinct customer names or addresses exist.
- Metrics for Column Profiling: Key metrics include the count of distinct values, frequency distribution of values, minimum and maximum values, and data type consistency. These metrics help in identifying patterns, outliers, and anomalies.
Column profiling is essential for understanding the variability and distribution of data in each column, which can highlight potential data quality issues such as unexpected or erroneous values.
Cross-Column Profiling
Cross-column profiling examines the relationships and dependencies between different columns in a dataset. This technique is critical for identifying correlations and ensuring data consistency.
- Definition and Importance: It involves comparing values between columns to check for consistency and logical relationships. For example, checking that the ‘date of birth’ column is consistent with the ‘age’ column in a customer dataset.
- Analyzing Relationships Between Columns: Cross-column profiling can detect dependencies and conditional patterns, such as ensuring that all entries with a certain value in one column have a corresponding expected value in another column.
Cross-column profiling ensures that the relationships between different fields in a dataset are logical and consistent, preventing errors in data analysis and reporting.
Cross-Table Profiling
Cross-table profiling focuses on analyzing relationships between different tables in a database, ensuring referential integrity and consistency.
- Definition and Examples: This technique checks that the data in one table corresponds correctly with data in another table. For example, ensuring that every order in the ‘Orders’ table has a corresponding entry in the ‘Customers’ table.
- Ensuring Referential Integrity and Data Consistency Across Tables: Cross-table profiling helps in maintaining referential integrity, ensuring that foreign keys correctly reference primary keys in related tables, thus preventing orphaned records and data integrity issues.
Maintaining referential integrity across tables is crucial for accurate data representation and avoiding inconsistencies in database operations.
Data Quality Profiling
Data quality profiling assesses various aspects of data to ensure it meets predefined quality standards. This technique focuses on metrics that define the overall quality of data.
- Key Metrics for Data Quality: Metrics include accuracy, completeness, consistency, and validity. These metrics are used to measure how well the data conforms to expected standards and rules.
- Examples and Best Practices: Examples include profiling to identify invalid email addresses in a contact list or checking for duplicate entries in a customer database. Best practices involve regularly profiling data to maintain high-quality standards.
By focusing on data quality profiling, organizations can proactively manage data issues, leading to improved data reliability and trustworthiness.
Data Completeness Profiling
Data completeness profiling evaluates whether all required data is present within a dataset. This technique identifies missing data and assesses the impact on analysis.
- Techniques for Assessing Completeness: Techniques include calculating the percentage of missing values, checking for mandatory fields, and analyzing the completeness of key business data attributes.
- Addressing Missing or Incomplete Data: Strategies to handle incomplete data include using data imputation techniques, flagging missing data for further investigation, and implementing validation checks to prevent data omissions.
Ensuring data completeness is critical for accurate analysis and decision-making, as missing data can lead to biased results and incomplete insights.
Data Consistency Profiling
Data consistency profiling ensures that data is uniform across different systems and databases, which is essential for integrated data environments.
- Ensuring Uniform Data Across Systems: This technique checks for consistent data formats, values, and definitions across multiple datasets. For example, ensuring that the same customer ID has the same details across different tables.
- Techniques for Identifying and Correcting Inconsistencies: Techniques include cross-referencing data entries, standardizing data formats, and using automated tools to detect and correct inconsistencies.
Maintaining data consistency across systems is crucial for accurate reporting, reliable analytics, and seamless data integration.
Common Data Profiling Tools
Data profiling tools help automate the process of analyzing and managing data quality. These tools come in various forms, ranging from open-source software to commercial solutions, each offering different features and capabilities.
1. Open-source Tools
Open-source data profiling tools are widely used due to their flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and community support. They provide essential features for data profiling and quality management.
- Overview of Popular Open-Source Data Profiling Tools: Some popular open-source tools include Apache Griffin, DataCleaner, and Talend Data Quality. These tools offer basic to advanced profiling capabilities suitable for small to large datasets.
- Pros and Cons of Using Open-Source Tools: Open-source tools are often free and customizable, making them accessible to organizations of all sizes. However, they may require more technical expertise to set up and maintain, and support might be limited compared to commercial tools.
Open-source tools are an excellent choice for organizations looking to implement data profiling without significant upfront costs, provided they have the technical resources to manage these tools.
2. Commercial Tools
Commercial data profiling tools offer more comprehensive features and professional support, making them suitable for enterprise-level data management.
- Overview of Leading Commercial Data Profiling Tools: Leading tools include IBM InfoSphere Information Analyzer, Informatica Data Quality, and SAS Data Quality. These tools offer advanced profiling capabilities, including automated data quality checks, integration with data governance frameworks, and support for large-scale data environments.
- Features, Benefits, and Use Cases of Each Tool: Commercial tools provide features like automated anomaly detection, detailed reporting, real-time monitoring, and integration with other enterprise data management solutions. They are commonly used in industries like finance, healthcare, and telecommunications, where data quality is critical.
While commercial tools involve higher costs, their robust features and professional support make them valuable investments for organizations needing scalable and reliable data quality solutions.
Steps to Implement Data Profiling
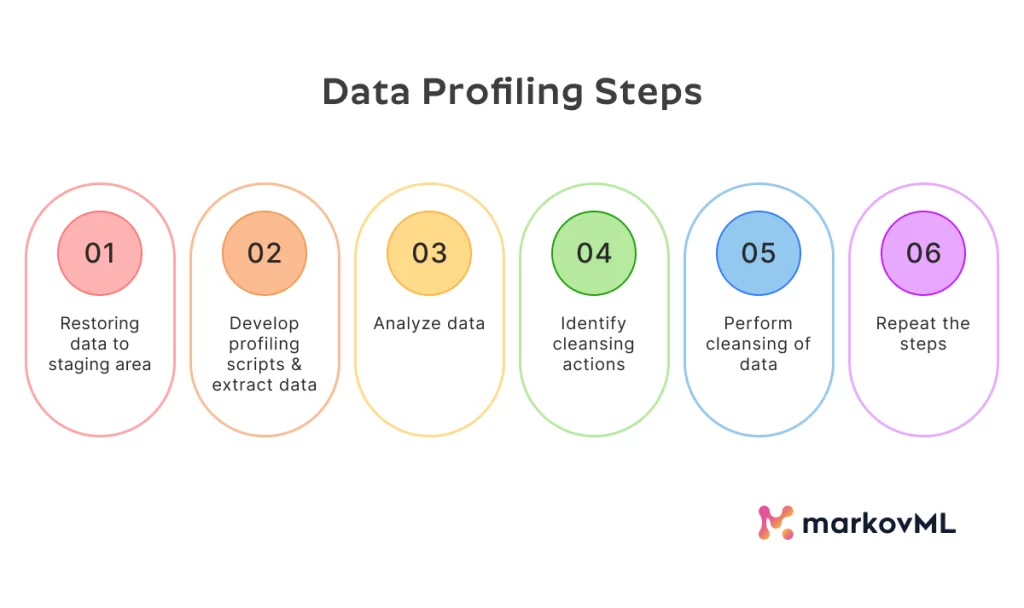
Implementing data profiling requires a systematic approach to ensure accuracy and comprehensiveness. The following steps outline a structured path for successful data profiling:
Define Clear Objectives
Establishing well-defined objectives is the first step in any data profiling initiative. Knowing what you want to achieve—be it improving data quality, supporting compliance, or enhancing data integration—sets the direction for the entire process.
- Align with Business Needs: Ensure that the objectives align with business goals and address specific data quality challenges.
- Set Measurable Targets: Define clear targets for metrics like data accuracy, completeness, and consistency.
Choose the Right Tools and Techniques
Selecting appropriate data profiling tools and techniques is critical for effective analysis. Consider factors such as data complexity, scale, and integration capabilities when choosing tools.
- Evaluate Options: Compare open-source and commercial tools to find the best fit for your data profiling needs.
- Match Techniques to Data Types: Use techniques like column profiling for individual data attributes and cross-table profiling for relationships across datasets.
Prepare Your Data
Before diving into profiling, prepare the data by ensuring it is accessible, clean, and ready for analysis. Proper preparation sets the stage for accurate profiling results.
- Data Collection: Gather data from relevant sources, ensuring you have access to all necessary datasets.
- Initial Cleansing: Perform basic data cleansing to remove obvious errors and inconsistencies.
Conduct the Profiling Analysis
Once the data is prepared, conduct a thorough profiling analysis. This step involves applying various profiling techniques to gain insights into the quality and structure of the data.
- Run Profiling Tests: Utilize techniques such as data quality profiling and data completeness profiling to analyze different aspects of the data.
- Generate Insights: Create detailed reports that highlight key findings, metrics, and areas needing improvement.
Review and Document Results
After profiling, review the findings to identify patterns, anomalies, and data quality issues. Documentation of these results is essential for tracking progress and implementing changes.
- Analyze Findings: Examine the results to understand the current state of data quality and any discrepancies.
- Keep Detailed Records: Document all findings, decisions, and corrective actions taken for future reference.
Implement Improvements
Based on the profiling results, take corrective actions to address data quality issues. Implementing improvements is crucial to maintaining high data standards.
- Correct Identified Issues: Fix errors, inconsistencies, and other data quality problems revealed during the profiling process.
- Enhance Processes: Improve data collection, storage, and management practices to prevent future issues.
Monitor Continuously
Data profiling is an ongoing activity. Regular monitoring and profiling help ensure data quality is maintained and adapt to any changes in data sources or business requirements.
- Schedule Regular Checks: Implement regular profiling sessions to continuously monitor data quality.
- Automate Monitoring: Use automation tools to track data quality metrics in real-time and respond to anomalies swiftly.
Best Practices for Data Profiling
Adhering to best practices in data profiling ensures effective data management and quality control. Below is a restructured approach to implementing these best practices:
Define Specific Goals
Setting specific and achievable goals at the outset is crucial for guiding the data profiling process and measuring its success.
- Align with Strategic Objectives: Ensure that profiling goals support broader business strategies.
- Focus on Key Data Metrics: Target specific metrics like data accuracy, consistency, and completeness.
Engage Stakeholders Early
Involving stakeholders throughout the data profiling process ensures that their needs are met and fosters collaboration.
- Collaborate with Business Users: Engage business users to understand their data requirements and concerns.
- Include IT and Data Teams: Involve technical teams for their expertise in data handling and tool usage.
Select Appropriate Techniques and Tools
The choice of data profiling techniques and tools should match the complexity of the data and the specific objectives of the profiling exercise.
- Assess Data Requirements: Choose profiling techniques based on the type of data and desired insights.
- Evaluate Tool Features: Consider the scalability, ease of use, and integration capabilities of profiling tools.
Regular Monitoring and Adjustment
Continuous monitoring and periodic reviews are essential to maintain data quality and address emerging issues.
- Implement Routine Checks: Schedule regular data profiling sessions to keep track of data quality.
- Adapt to Changes: Be flexible and adjust profiling techniques as data sources and business needs evolve.
Document Findings and Actions
Documentation is a key part of the data profiling process, providing a record of findings and decisions that support continuous improvement.
- Keep Comprehensive Records: Document all steps of the profiling process, including methodologies, findings, and actions taken.
- Report to Stakeholders: Use clear and concise reports to communicate profiling results and recommendations to stakeholders.
Challenges and Solutions in Data Profiling
Data profiling, while essential for maintaining high data quality standards, comes with its own set of challenges. Overcoming these obstacles is crucial to ensure effective data management and reliable data insights. Below are some of the common challenges faced in data profiling and potential solutions to address them.
Data Volume and Complexity
Handling large volumes of data from various sources can be overwhelming. As organizations grow, so does the amount of data they generate, often leading to complex data structures. This complexity makes it difficult to profile data efficiently, as different types of data (structured, unstructured, and semi-structured) require different profiling techniques.
- Scalability Issues: Profiling vast datasets can lead to performance bottlenecks, slowing down the process and consuming significant computational resources.
- Solution: Implement scalable data profiling tools that can handle large datasets efficiently. Utilize distributed computing frameworks, such as Apache Hadoop or Spark, to parallelize data profiling tasks and manage big data effectively.
Data Privacy and Security
With increasing concerns about data privacy and security, organizations must balance data quality initiatives with compliance requirements. Profiling sensitive data, such as personal identification information (PII), requires strict adherence to privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
- Privacy Concerns: Profiling sensitive data can lead to unauthorized access or exposure of confidential information if not handled properly.
- Solution: Employ data anonymization and masking techniques during the profiling process to protect sensitive information. Use secure data profiling tools that offer built-in privacy controls and comply with data protection regulations.
Tool Limitations
Not all data profiling tools offer the same level of functionality, leading to limitations in handling specific data types or profiling techniques. Organizations may find that existing tools do not support advanced profiling needs or cannot integrate seamlessly with their existing systems.
- Tool Constraints: Limited features and lack of compatibility with existing data management systems can hinder effective data profiling.
- Solution: Evaluate and choose data profiling tools based on specific organizational needs. Opt for tools that offer flexibility, extensibility, and integration capabilities to work with diverse data environments. Consider open-source tools for customization options.
Continuous Data Quality Management
Maintaining high data quality is not a one-time task but requires continuous monitoring and management. Data quality can deteriorate over time due to data decay, changes in data sources, or evolving business requirements.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Ensuring data remains accurate, consistent, and relevant over time is a continuous challenge.
- Solution: Implement automated data quality monitoring systems that regularly check for anomalies and inconsistencies. Schedule routine data profiling activities to detect and address data quality issues proactively.
Real-world Applications of Data Profiling
Data profiling has become an integral part of various industries, enabling organizations to ensure data quality, support compliance, and improve operational efficiency. Here are some real-world applications of data profiling across different sectors:
Healthcare
In the healthcare industry, data profiling is essential for managing patient records, ensuring regulatory compliance, and enhancing the quality of care. Accurate and complete patient data is critical for effective treatment and healthcare management.
- Patient Data Management: Data profiling helps in identifying inaccuracies in patient records, such as incorrect personal details or missing medical history, which can lead to better patient care.
- Regulatory Compliance: Profiling data ensures that healthcare organizations meet compliance requirements for data privacy and security, such as HIPAA regulations.
Pointers for Healthcare:
- Improving diagnostic accuracy with high-quality patient data.
- Enhancing patient outcomes through better data integration.
- Streamlining healthcare operations with accurate data reporting.
Finance
Data profiling plays a pivotal role in the finance industry by enhancing the accuracy of transaction data, detecting fraudulent activities, and ensuring compliance with financial regulations. Financial institutions rely on high-quality data to manage risks and make informed investment decisions.
- Transaction Data Accuracy: Profiling transaction data helps in identifying discrepancies, reducing errors, and ensuring accurate financial reporting.
- Fraud Detection: Data profiling techniques, such as cross-column profiling, are used to detect unusual patterns that may indicate fraudulent activities.
Pointers for Finance:
- Improving risk management with accurate data.
- Enhancing customer trust by ensuring data integrity.
- Supporting compliance with financial regulations.
Retail
In the retail sector, data profiling is used to manage inventory, optimize customer data quality, and enhance marketing strategies. Retailers rely on accurate data to understand customer behavior, manage stock levels, and personalize shopping experiences.
- Inventory Management: Data profiling ensures that inventory data is accurate, which helps in reducing stockouts and overstock situations.
- Customer Data Quality: Profiling customer data helps retailers maintain accurate contact information, preferences, and purchase history, enabling personalized marketing.
Pointers for Retail:
- Improving sales forecasting with reliable data.
- Enhancing customer satisfaction through accurate personalization.
- Reducing operational costs by optimizing inventory management.
Telecommunications
Telecommunication companies use data profiling to manage customer data, optimize network performance, and improve service delivery. Accurate data is essential for maintaining customer satisfaction and operational efficiency in a highly competitive industry.
- Network Performance Optimization: Profiling data helps in identifying network issues, optimizing bandwidth usage, and ensuring high-quality service delivery.
- Customer Data Management: Accurate profiling of customer data ensures better service personalization, accurate billing, and effective customer support.
Pointers for Telecommunications:
- Enhancing customer experience with reliable service.
- Reducing network downtime with accurate data insights.
- Supporting targeted marketing campaigns with high-quality customer data.
By addressing the challenges in data profiling and leveraging its applications effectively, organizations across various industries can enhance data quality, support compliance, and drive better decision-making, ultimately leading to improved business outcomes.
The Role of Data Profiling in Data Quality
Data profiling plays a critical role in ensuring data quality within organizations. By analyzing and understanding data sets at a granular level, data profiling helps to identify inaccuracies, inconsistencies, and anomalies. This, in turn, enables organizations to take corrective actions and maintain high data integrity. Effective data profiling is the first step towards building a reliable data environment that supports accurate analytics, decision-making, and reporting.
- Data Accuracy: Profiling helps to identify errors and discrepancies in data, ensuring that the information used for decision-making is accurate.
- Data Consistency: By checking for uniformity across different data sets, data profiling ensures that all data conforms to predefined formats and standards.
- Data Completeness: Profiling helps in identifying missing values and incomplete records, enabling data quality teams to address these gaps.
- Data Validity: Ensures that data entries conform to the rules and standards set by the organization.
Importance of Data Profiling for Maintaining Data Integrity
Maintaining data integrity is crucial for businesses to make reliable decisions. Data profiling helps by ensuring that data is consistent and accurate, which in turn supports data integrity. Profiling identifies incorrect or outdated data and helps in cleansing and updating data sets, which maintains the reliability of data sources.
- Supports Accurate Decision-Making: Accurate data enhances the reliability of insights and predictions.
- Prevents Data Corruption: Regular profiling reduces the risk of data corruption and maintains data reliability over time.
How Data Profiling Supports Data Governance
Data profiling is an essential component of data governance frameworks. It helps in establishing data quality standards, monitoring compliance, and ensuring that data practices align with regulatory requirements. By profiling data regularly, organizations can maintain high standards of data integrity and security.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensures that data meets regulatory requirements such as GDPR and CCPA.
- Standardization: Helps maintain consistency across data sets and support data governance policies.
Case Studies of Improved Data Quality Through Profiling
Numerous organizations have successfully improved their data quality by implementing robust data profiling practices. These case studies demonstrate how data profiling can lead to significant improvements in accuracy, completeness, and reliability, resulting in better decision-making and operational efficiency.
- Healthcare: A hospital improved patient data accuracy by implementing regular data profiling, which reduced errors in patient records and enhanced patient care.
- Retail: A retail company used data profiling to clean its customer database, resulting in more accurate targeted marketing campaigns and increased customer satisfaction.
Future Trends in Data Profiling
As data continues to grow in volume and complexity, data profiling techniques and tools are evolving to keep pace. The future of data profiling is set to be shaped by advancements in AI, real-time analytics, cloud computing, and privacy regulations. These trends will not only enhance the efficiency of data profiling but also ensure that data quality management is aligned with modern data management practices.
- AI and Machine Learning: Automation of profiling processes, enabling quicker and more accurate data quality assessments.
- Real-Time Profiling: Increasing need for real-time data quality assessments as businesses shift towards real-time analytics.
- Cloud-Based Solutions: Scalability and flexibility offered by cloud-based profiling tools are making them popular choices for modern enterprises.
- Privacy-Driven Profiling: With rising concerns about data privacy, data profiling is evolving to include privacy-preserving techniques.
AI and Machine Learning in Data Profiling
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are transforming data profiling by automating the detection of anomalies and predicting potential data quality issues. These technologies help in processing large volumes of data efficiently, enhancing the accuracy and speed of profiling tasks.
- Automated Profiling: AI algorithms can automatically detect patterns and anomalies, reducing the need for manual intervention.
- Predictive Profiling: Machine learning models can predict future data quality issues, allowing proactive measures.
Real-Time Data Profiling
The need for real-time data processing is driving the demand for real-time data profiling. Organizations require instant insights and the ability to assess data quality as it is being generated. This approach helps in making quicker decisions and responding to changes promptly.
- Instant Data Quality Checks: Allows for immediate detection of errors and inconsistencies.
- Supports Real-Time Decision-Making: Real-time profiling ensures that data is up-to-date and reliable for immediate analysis.
Cloud-Based Data Profiling Solutions
With the shift towards cloud computing, cloud-based data profiling solutions offer scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency. These solutions provide robust data profiling capabilities that can handle large-scale data processing and are accessible from anywhere.
- Scalability: Easily scales to accommodate growing data volumes.
- Flexibility: Offers seamless integration with cloud-based data storage and analytics platforms.
Privacy-Driven Data Profiling
As data privacy concerns grow, data profiling is increasingly incorporating privacy-preserving techniques. This ensures that data profiling activities comply with regulations and protect sensitive information from unauthorized access.
- Data Anonymization: Implementing anonymization techniques to protect sensitive data during profiling.
- Compliance Monitoring: Regularly checking profiling practices against privacy regulations.
Conclusion
Data profiling is a critical practice that enhances data quality, supports compliance, and improves decision-making across various industries. As organizations continue to generate and rely on vast amounts of data, the importance of maintaining high data quality through effective profiling techniques cannot be overstated. With the advancement of AI, real-time profiling, and cloud-based solutions, data profiling practices are set to evolve, making it easier for businesses to manage their data efficiently.
Recap of the Importance of Data Profiling
Data profiling is essential for ensuring the accuracy, consistency, and reliability of data. By regularly profiling their data, organizations can maintain high data quality standards, support regulatory compliance, and make informed decisions.
The Future Outlook of Data Profiling in Data Management
The future of data profiling will be shaped by emerging technologies such as AI and machine learning, real-time analytics, and cloud computing. These advancements will enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of data profiling, enabling organizations to maintain high data quality in an increasingly complex data environment.
Final Thoughts on Implementing Effective Data Profiling Practices
Implementing effective data profiling practices requires a strategic approach, the right tools, and continuous monitoring. Organizations can achieve better business outcomes and maintain a competitive edge in the data-driven world by prioritizing data quality and investing in robust profiling techniques.
What is Data Profiling?
Data profiling is the process of examining data from existing sources and collecting statistics or summaries to understand its structure, quality, and consistency. It helps identify potential issues and areas for improvement.
Why is Data Profiling Important?
Data profiling is important because it helps ensure that data is accurate, consistent, and reliable. This is essential for making informed business decisions, supporting compliance, and improving operational efficiency.
What Tools are Used for Data Profiling?
Common data profiling tools include open-source platforms like Talend Open Studio, commercial solutions like Informatica Data Quality, and cloud-based options such as Microsoft Azure Data Catalog.
How Does Data Profiling Improve Data Quality?
Data profiling improves data quality by identifying inaccuracies, inconsistencies, and missing values in data sets. It allows organizations to take corrective actions to enhance data accuracy and reliability.
What are the Challenges in Data Profiling?
Challenges in data profiling include handling large volumes of data, ensuring data privacy and security, managing tool limitations, and maintaining continuous data quality management.